 |
absggn00000298
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) OPERATION [F2]
id014094101200
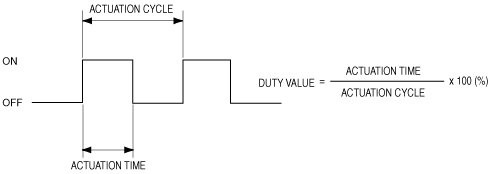
Duty Control
Operation outline
absggn00000298
|
IAC valve actuation time
Target airflow
Control Zone
Control outline
absggn00000231
|
Start zone
Initial setting zone
Closed loop zone
Open loop zone
Corrections
|
Item |
Purpose |
Conditions |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
BARO correction
|
To adjust intake air amount according to BARO change
|
According to BARO
|
Lower BARO → Larger correction
|
|
After-start correction
|
To stabilize engine speed just after engine start
|
Just after engine start
|
Lower ECT → Larger correction
Lower IAT → Larger correction
|
|
Load correction
|
To stabilize engine speed when A/C or P/S operating
|
A/C or P/S turned on
|
Heavier load → Larger correction
|
|
Dashpot correction
|
To reduce deceleration shack and CO and HC emission Leaves during deceleration
|
Just after deceleration at CTP
|
High engine speed → Larger correction
|
|
Deceleration volume increase correction
|
To reduce engine speed drop when decelerating
|
When deceleration (Throttle opening angle variation large)
|
Deceleration → Set amount of correction
|
|
Acceleration volume decrease correction
|
To reduce sudden engine speed increase when accelerating
|
When accelerating (Throttle opening angle variation large))
|
Acceleration → Set amount of correction
|
|
Closed loop correction
|
To bring engine speed to target speed
|
When in closed loop zone and open loop zone
|
Larger difference → Larger correction
|
|
Learning correction
|
To correct target speed
|
When in closed loop zone and open loop zone
|
—
|