1. Introduction to the trouble diagnosis of engine
1. Engine control system check
Perform the Engine control system check.
Refer to "51.Engine Control 1A.Troubleshooting(RZ4E-TC) Diagnostic system check-engine controls".
The following can be determined by way of the engine control system check.
- Identification of the control module command system
- Capacity of the control modules that communicate through the serial data circuit
- Identification of all stored diagnostic trouble codes and their statuses
2. Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
1. Reading flashing DTCs (Except Euro4)
Note
- The flash codes do not apply to Euro4 models.
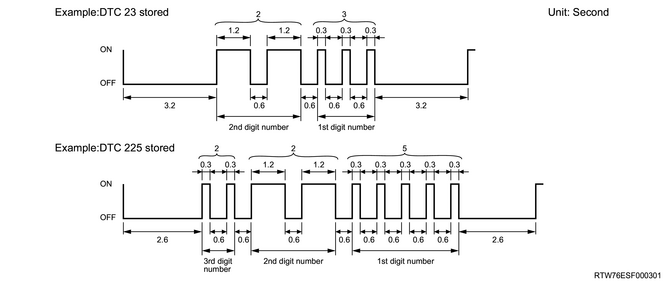
The equipment for communicating with the control unit is the data link connector (DLC). The DTCs stored in the ECM memory can be read either by connecting a hand-held diagnostic scanner, such as a scan tool, with the DLC, or by counting the number of the SVS indicator light flashes when the diagnostic test terminal of the DLC is grounded.
Short-circuit DLC pin 4 and pin 12. Turn ON the ignition switch without starting the engine. If the SVS indicator light flashes 3 times, this indicates that there is a current failure DTC or a DTC in the failure history. When 2 or more DTCs have been stored in the ECM memory, the DTCs are displayed 3 times, each in ascending order of DTC number. This display continues while the DLC terminals are short-circuited.
2. DTC type definition (Euro4)
There are 4 DTC types: Type A, B, C, and D. Among these DTCs, type A and B DTCs are related to emission whereas type C and D DTCs are related to items other than emission.
3. DTC type definition (Except Euro4)
There are 3 DTC types: Type A, B, and D. Among these DTCs, type A and B DTCs are related to emission whereas type D DTCs are related to items other than emission.
4. Action taken when DTC sets - Type A (Except Euro4)
- The ECM illuminates the check engine warning light when the diagnostic runs and fails.
5. Action taken when DTC sets - Type B (Except Euro4)
- The ECM illuminates the check engine warning light after 2 consecutive driving cycles when the diagnostic runs and fails.
- The ECM records the operating conditions when the diagnostic runs and fails. The first time the diagnostic runs and fails, the ECM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure in 2 consecutive driving cycles, the ECM records the operating conditions at the time of failure, stores this information in the Freeze Frame, and updates the Failure Records.
6. Condition for clearing the check engine warning light/DTC - Type A or Type B (Except Euro4)
- The ECM turns OFF the check engine warning light after 1 ignition cycle when the diagnostic runs and does not fail.
- A current DTC is cleared when the diagnostic runs and passes.
- A DTC history is cleared after 40 consecutive driving cycles if no failures are reported.
- Clear the check engine warning light and the DTC with a scan tool.
7. Action taken when DTC sets - Type D (Except Euro4)
- The ECM does not illuminate the check engine warning light.
8. Action taken when DTC sets - Type A (Euro4)
- The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicator light (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails.
- The ECM records the operating conditions when the diagnostic runs and fails. The ECM stores this information in the Freeze Frame/Failure Records.
9. Action taken when DTC sets - Type B (Euro4)
- The ECM illuminates the MIL after 2 consecutive driving cycles when the diagnostic runs and fails.
- The ECM records the operating conditions when the diagnostic runs and fails. The first time the diagnostic runs and fails, the ECM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure in 2 consecutive driving cycles, the ECM records the operating conditions at the time of failure, stores this information in the Freeze Frame, and updates the Failure Records.
10. Condition for clearing the MIL/DTC - Type A or Type B (Euro4)
- The ECM turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive driving cycles when the diagnostic runs and does not fail.
- A current DTC is cleared when the diagnostic runs and passes.
- The DTC history is cleared after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles if no failures are reported.
- Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool.
11. Action taken when DTC sets - Type C (Euro4)
- The ECM illuminates the service vehicle soon (SVS) indicator light when the diagnostic runs and fails.
- The ECM records the operating conditions when the diagnostic runs and fails. The ECM stores this information in the Failure Records.
12. Condition for clearing the SVS indicator light/DTC - Type C (Euro4)
- The ECM turns OFF the SVS indicator light after 1 driving cycle when the diagnostic runs and does not fail.
- A current DTC is cleared when the diagnostic runs and passes.
- The DTC history is cleared after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles if no failures are reported.
- Clear the SVS indicator light and the DTC with a scan tool.
13. Action taken when DTC sets - Type D (Euro4)
- The ECM does not illuminate the MIL or SVS indicator light.
- The ECM records the operating conditions when the diagnostic runs and fails. The ECM stores this information in the Failure Records.
14. Condition for clearing the DTC - Type D
- A current DTC is cleared when the diagnostic runs and passes.
- The DTC history is cleared after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles if no failures are reported.
- Clear the DTC with a scan tool.
3. Oral consultation
1. Questioning
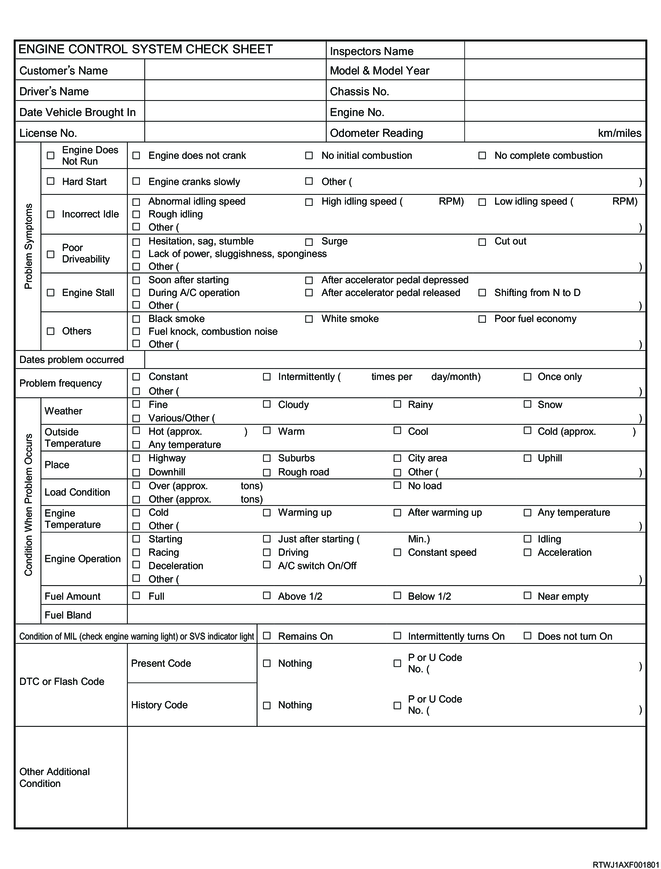
The engine control system check is used to check the locations of the correct procedures and steps for diagnosis of the system.
The engine control system check sheet must be used to verify customer complaints. It is necessary to understand the correct system operations and to verify that the customer complaint is in fact a malfunction of the system.
Engine control system check sheet