1. Checking the air conditioning system using the manifold gauge
1. Inspection conditions
- Surrounding ambient temperature is approx. 30 to 35°C {86 to 95°F}.
- The engine speed is approx. 1500 rpm.
- The blower motor is HIGH.
- The temperature is set to MAX COOL.
- All the doors are closed.
- Inside air recirculation is selected.
2. Normal pressure (reference)
127 to 245 kPa { 1.3 to 2.5 kgf/cm2 / 18 to 36 psi } Low pressure side
1,373 to 1,667 kPa { 14 to 17 kgf/cm2 / 199 to 242 psi } High pressure side
3. Manifold gauge connection
- Low pressure hose to intake side
- High pressure hose to outlet side
AS HFC-134a is employed in the air conditioner system of this vehicle when checking the air conditioner system, make sure to use air conditioner servicing tools, such as manifold gauge and charging hose, that are intended for use with HFC-134a.
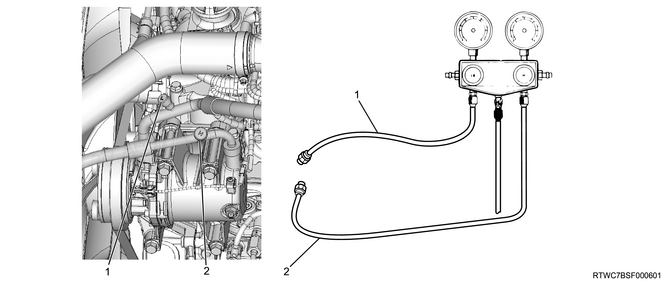
Legend
- Low pressure side
- High pressure side
4. Failure conditions, causes, and actions
1) Status
- Cooling is insufficient.
- Both the high- and low-pressure values are low.
- Gas bubbles are continuously observed through the sight glass.
- The temperature of the air blown out does not decrease.
49 to 98 kPa { 0.5 to 1.0 kgf/cm2 / 7 to 14 psi } Low pressure side
686 to 981 kPa { 7.0 to 10.0 kgf/cm2 / 99 to 142 psi } High pressure side
Cause
- The refrigerant level is insufficient due to a refrigerant leakage.
Treatment
- Inspect and repair the refrigerant leakage.
- Fill the refrigerant up to the specified level.
2) Status
- Cooling is insufficient.
- Both the high- and low-pressure values are high.
- No gas bubbles are observed through the sight glass even after lowering the engine speed.
- The temperature of the air blown out does not decrease.
245 to 294 kPa { 2.5 to 3.0 kgf/cm2 / 36 to 43 psi } Low pressure side
2,256 to 2,452 kPa { 23.0 to 25.0 kgf/cm2 / 327 to 356 psi } High pressure side
Cause
- The refrigerant is over-filled.
- The cooling of the condenser is insufficient.
Treatment
- Inspect the refrigerant level and fill to the specified level.
- Clean the condenser.
- Inspect and repair the condenser fan.
3) Status
- Cooling is insufficient.
- Both the high- and low-pressure values are high.
- The pipe at the low pressure side is not cold.
- Gas bubbles pass through the sight glass.
245 to 294 kPa { 2.5 to 3.0 kgf/cm2 / 36 to 43 psi } Low pressure side
2,256 to 2,452 kPa { 23.0 to 25.0 kgf/cm2 / 327 to 356 psi } High pressure side
Cause
- The A/C cycle contains air due to insufficient evacuation.
Treatment
- Evacuate and fill with the specified amount of refrigerant.
4) Status
- Cooling is insufficient.
- Both the high- and low-pressure values are high.
- Frosting occurs at the low pressure side pipe.
294 to 392 kPa { 3.0 to 4.0 kgf/cm2 / 43 to 57 psi } Low pressure side
1,961 to 2,452 kPa { 20.0 to 25.0 kgf/cm2 / 284 to 356 psi } High pressure side
Cause
- Expansion valve malfunction
Treatment
- Inspect the installation status of the thermosensor. If no abnormal condition is found, replace the expansion valve.
5) Status
- It is not cold.
- The pressure at the low pressure side is too high, while the pressure at the high pressure side is too low.
- The high and low pressures balance immediately after turning OFF the A/C.
392 to 588 kPa { 4.0 to 6.0 kgf/cm2 / 57 to 85 psi } Low pressure side
686 to 1,079 kPa { 7.0 to 11.0 kgf/cm2 / 99 to 156 psi } High pressure side
Cause
- There is compression failure due to a defective compressor.
Treatment
- Compressor replacement
6) Status
- Cooling is inconsistent.
- The pressure at the low pressure side becomes a vacuum at times, and the pressure at the high pressure side also drops but is normal in other instances.
- Immediately after the A/C starts operating, it functions normally, but the pressure at the low pressure side indicates a vacuum after a while.
0 to 127 kPa { 0.0 to 1.3 kgf/cm2 / 0 to 18 psi } Low pressure side
588 to 1,765 kPa { 6.0 to 18.0 kgf/cm2 / 85 to 256 psi } High pressure side
Cause
- When moisture enters the A/C cycle, it freezes in the expansion valve and the cycle may be blocked, returning to normal after thawing.
Treatment
- Expansion valve replacement
- Replace the receiver dryer and the compressor oil.
- Evacuate and fill with the specified amount of refrigerant.
7) Status
- Cooling is inconsistent.
- The pressure at the low pressure side results in a vacuum, and the pressure at the high pressure side is also low.
- The low pressure side is a vacuum.
- There is frost on the front and back pipe connections of the receiver dryer or the expansion valve, and there is a large temperature difference on the IN side and OUT side of the trouble area.
490 to 588 kPa { 5.0 to 6.0 kgf/cm2 / 71 to 85 psi } High pressure side
Cause
- The cycle is blocked due to freezing of moisture or the presence of foreign material.
- The cycle is blocked due to a defective expansion valve thermosensor.
- If the cycle is completely clogged, a vacuum appears immediately, whereas if it is slightly clogged, the pressure drops gradually to a vacuum.
Treatment
- When moisture enters the cycle, replace the receiver dryer and change compressor oil, and fill the refrigerant up to the specified level.
- If the thermosensor is defective, replace the expansion valve.