MULTIPLE FUEL INJECTION CONTROL [SKYACTIV-D 2.2]
id0140z7988100
Outline
• A multiple fuel injection control has been adopted which divides the injection times into several stages for suppressing the generation of particulate matter/NOx, improved combustion stability, and combustion noise reduction.
-
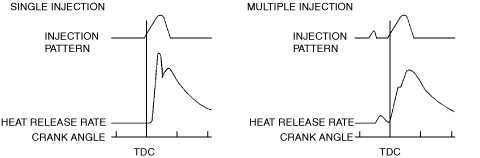
― For single injection, the injected fuel is combusted rapidly, and particulate matter/NOx and combustion noise worsen because the required fuel is injected at once.
― For multiple injection, the combustion is sluggish and particulate matter/NOx and combustion noise are suppressed because the required fuel is injected over several stages.
• The PCM injects fuel several times prior to the main injection according to the vehicle operation conditions. (Pilot injection)
• During diesel particulate filter generation control, fuel is injected after the main injection to increase the temperature. (Follow-up injection, post injection)
Block diagram
Operation
• The PCM determines the number of fuel injections based on the fuel injection amount and signals from each sensor.
• When the engine is started, the number of fuel injections is determined by the engine coolant temperature and the engine speed.
• In the multiple fuel injection control, there are various patterns from the combination of the number of fuel injections.
• The PCM selects the optimum pattern based on the vehicle conditions and performs fuel injection for a maximum of 8 times.
|
Control range
|
Control description
|
|
Constant fuel injection
|
Low engine speed, low load
|
For the purpose of reducing engine knock occurring during combustion and to assure ignitability, the number of fuel injections is increased to a maximum of 6 times.
|
|
High engine speed, high load
|
Output and fuel consumption is improved by reducing the fuel injection time and injecting a higher amount of fuel over a fewer number of injections.
|
|
Rapid engine warm-up control
|
When the engine coolant temperature is low and the cabin heating performance is insufficient, 2 additional follow-up injections are performed to increase the exhaust temperature from the after-burn.
|
|
Diesel particulate filter regeneration control
|
During diesel particulate filter regeneration, fuel injection is performed at a slower timing than normal to remove particulate matter (PM) accumulated in the diesel particulate filter.
1. Follow-up injection is performed after the main injection. (increases exhaust pipe temperature)
2. Post injection is performed 1—5 times* (increases exhaust temperature necessary for combustion and removal of particulate matter (PM))
|
|
Fuel-cut
|
During fuel-cut operation, fuel is not injected by the fuel injection amount control.
|
* :When the unburned fuel (HC) caused by the post injections reaches the oxidation catalytic converter, it is activated at the catalyst, and the exhaust gas temperature is increased. The division of the post injection into 1—5 times is for the purposes of reducing engine oil dilution and fuel adhesion to the cylinder walls. If fuel injection is performed at a slower timing than normal (timing in which no combustion occurs in cylinder), the fuel flows to the oil pan, and there is the possibility of the engine oil becoming diluted. In addition, by injecting small amounts of fuel in multiple stages, the penetration power of the atomized fuel is reduced and adhesion of fuel to the cylinder wall is prevented.
Regarding engine oil dilution from post injection
-
• Although post injection, in which fuel injection occurs after the combustion process, is effective for diesel particulate filter regeneration control by after-burn, fuel adhesion to the inside of the cylinder wall occurs with the possibility of engine oil dilution.
• As for the symptoms of engine oil dilution, use the guidelines indicated in the table below. (The engine oil level changes dramatically depending on the oil temperature and the amount of time elapsed since the engine was turned off, thus there may be differences in the actual engine oil level.))
|
Item
|
Engine oil dilution
|
|
Engine oil dilution amount reference
|
 |
|
Oil level gauge position
|
A
|
B
|
C
|
D
|
|
Instrument cluster (type A)
Message displayed in multi-information display
Instrument cluster (type B)
Engine oil warning light
|
No problem
|
—
|
Instrument cluster (type A)
“Engine Oil Pressure Inspection Required”
Instrument cluster (type B)
Illuminated
|
|
Check engine light
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
|
DTC recorded in PCM
|
P252F:00
|
P253F:00
|
|
Diesel particulate filter regeneration control range (auto diesel particulate filter regeneration control)
|
—
|
Diesel particulate filter regeneration control range (auto diesel particulate filter regeneration control)
|
|
User action
|
—
|
Vehicle servicing at Authorized Mazda Dealer
|
|
Action taken by servicing at Authorized Mazda Dealer
|
—
|
Action A
|
Action B
|
-
Action A
-
• If DTC P253F:00 is stored in the PCM, replace the engine oil and reset the engine oil data using the Mazda Modular Diagnostic System (M-MDS) even if the engine oil level is lower than the X mark on the oil level gauge.
-
Action B
-
• After verifying the engine oil level, replace the engine oil and implement the engine oil data reset using the Mazda Modular Diagnostic System (M-MDS).