ABS CONTROL
id041900701600
Outline
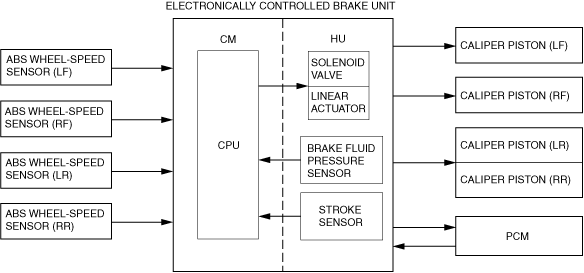
• ABS control occurs when wheel slip is determined by the CM part of the electronically controlled brake unit (based on the 4 electronically controlled brake unit wheel-speed sensors). Then, the electronically controlled brake unit HU linear actuator, and outlet and inlet solenoid valves are operated and brake fluid pressure is controlled accordingly to prevent wheel lock-up.
Features
• Use of ABS control during emergency braking or on slippery road surfaces allows directional stability to be maintained, steerability ensured and stopping distance to be reduced.
• The ABS control has an independent control system.
Construction
Block diagram
Operation
• During braking, ABS control occurs when wheel slip is determined by the CM part of the electronically controlled brake unit (based on signal from ABS wheel-speed sensor). Then, the CM part of the electronically controlled brake unit operates the electronically controlled brake unit HU linear actuator, and outlet and inlet solenoid valves and the brake fluid pressure is decreased and maintained according to the wheel slip condition. In addition, if the vehicle wheels return to the normal condition, the brake fluid pressure is increased and maintained so that the vehicle wheels operate to obtain stabilized braking force at all times.
Operation status transition diagram