TCS CONTROL
id041900701800
Outline
• The TCS control actuates torque reduction through engine control, as well as using brake control to control traction.
-
Note
-
• Engine control: Engine output is lowered by fuel cut and ignition timing control to reduce the traction, preventing driving wheel slip.
• Brake control: Brake fluid is pressurized from the electronically control brake unit against the driving wheel that is slipping to apply the brakes, preventing driving wheel slip.
Features
• The left and right wheels are controlled at the same time by engine control. Therefore, when the road surface friction coefficients differ between the left and right wheels, proper torque reduction cannot be performed separately for each wheel. When this occurs, torque reduction is performed by independent left and right wheel brake control, providing more stable vehicle control.
• The TCS OFF switch allows the driver to optionally enable/disable the TCS control at the driver's discretion. (2WD)
-
― When both wheels are stuck, the TCS control is inhibited to control the driving force by the driver's operation.
― The TCS control returns to normal operation automatically at the next ignition cycle.
Construction
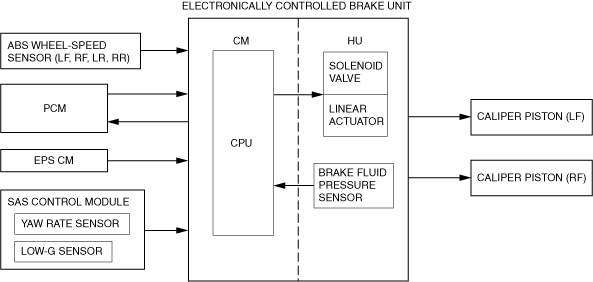
Block Diagram
Operation
• TCS control detects driving wheel spin based on the signals listed below, sends torque reduction request signals to the PCM, and also controls the solenoid valves and linear actuator in the electronically controlled brake unit.
-
― Wheel speed signals from front and rear ABS wheel-speed sensor
― Engine torque signal from the PCM
― Steering angle signal from EPS CM
― Yaw rate and lateral-G signals from SAS control module
― Fluid pressure signal from brake fluid pressure sensor (built into the electronically controlled brake unit)