DSC CONTROL
id041900701900
Outline
• Normally, the vehicle makes stable turn according to the steering wheel operation, however, a tire may exceed the limit of its gripping power in the lateral direction depending on the road conditions, vehicle speed, or the effect of sudden steering wheel operation during emergency maneuvering.
• The following 2 points can be considered as a situation in which a tire exceeds the limit of its gripping power in the lateral direction.
-
― Strong oversteer tendency: Rear wheel is in the process of losing gripping power relative to front wheel.
― Strong understeer tendency: Front wheel is in the process of losing gripping power relative to rear wheel.
• When the vehicle speed is approx. 15 km/h {9.3 mph} or more, the DSC operates. When the vehicle is under any of the situations above, the engine is output and the brakes of each wheel are controlled to suppress the oversteer or understeer tendency.
Function
Vehicle condition determination
-
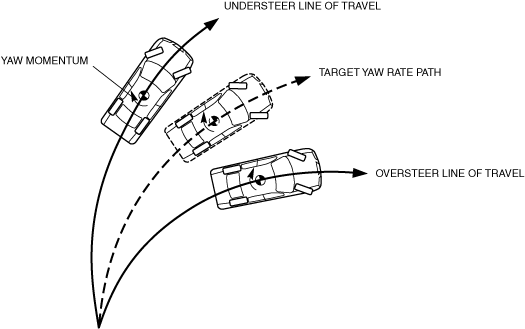
• The vehicle conditions are determined by detecting the wheel speed, the steering angle, the vehicle lateral G, and the vehicle yaw rate using each sensor, and calculations made by the electronically controlled brake unit. At this time, the oversteer tendency or the understeer tendency is determined by the difference between the target yaw rate value calculated from each sensor, and the value detected by the yaw rate sensor.
Oversteer tendency determination
-
• If the actual vehicle yaw rate is larger than the target yaw rate when the driver operates the steering wheel, it means that the vehicle is spinning or about to be spun. Therefore, it is determined that the vehicle tends to oversteer.
Understeer tendency determination
-
• If the actual vehicle yaw rate is less than the target yaw rate when the driver operates the steering wheel, it means that the vehicle is not be turned sufficiently. Therefore, it is determined that the vehicle tends to understeer.
Construction
Block diagram
Operation
• If the electronically controlled brake unit determines that the vehicle is under a strong oversteer tendency or strong understeer tendency, engine output is decreased and the vehicle yaw moment is controlled by applying braking force to the front or rear wheels to suppress the oversteer tendency or the understeer tendency.
Oversteer tendency suppression
-
• When a large oversteer tendency is determined, braking is applied to the outer front wheel according to the degree of the tendency. As a result, a yaw moment is formed towards the outer side of the vehicle and the oversteer tendency is suppressed.
Understeer tendency suppression
-
• When a large understeer tendency is determined, engine output is controlled and braking is applied to the inner rear wheel according to the degree of the tendency. As a result, a yaw moment is formed towards the inner side of the vehicle and the understeer tendency is suppressed.