 |
am2zzn00005060
HYDRAULIC VARIABLE VALVE TIMING CONTROL [SKYACTIV-G 1.3, SKYACTIV-G 1.5]
id0140q1318000
Without coolant control valve (4-1 exhaust system)
Outline
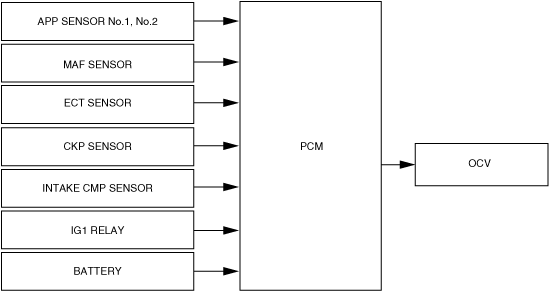
Block Diagram
am2zzn00005060
|
Operation
Range mode table
|
Mode name |
Control description |
|---|---|
|
Feedback mode
|
• The feedback mode constantly monitors whether the target intake valve timing is the determined value according to the engine operation conditions and controls the OCV drive current based on the results.
Mode execution condition
|
|
Cleaning mode
|
• Cleaning mode is to remove foreign matter in the OCV oil passages.
Mode execution condition
|
|
Cam retard mode
|
• If the cam retard is appropriate according to engine operation conditions such as while in torque down execution during idling, the cam retard mode retards the intake valve timing and stabilizes the engine speed.
Mode execution condition (without coolant control valve)
Mode execution condition (with coolant control valve)
|
Without coolant control valve (4-2-1 exhaust system), with coolant control valve
Outline
Block Diagram
am2zzn00004965
|
Operation
Range mode table
|
Mode name |
Control description |
|---|---|
|
Feedback mode
|
• The feedback mode constantly monitors whether the target exhaust valve timing is the determined value according to the engine operation conditions and controls the OCV drive current based on the results.
Mode execution condition
|
|
Cleaning mode
|
• Cleaning mode is to remove foreign matter in the OCV oil passages.
Mode execution condition
|
|
Cam advance mode
|
• If the cam advance is appropriate according to engine operation conditions such as while in torque down execution during idling, the cam advance mode advances the exhaust valve timing and stabilizes the engine speed.
Mode execution condition (without coolant control valve)
Mode execution condition (with coolant control valve)
|