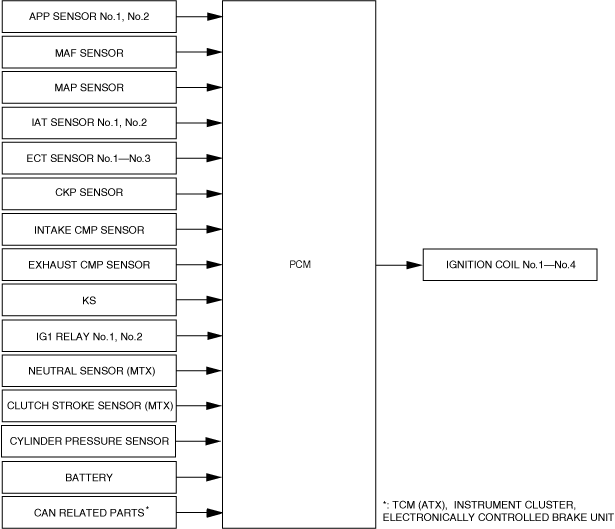
 |
ac30zn00001354
ELECTRONIC SPARK ADVANCE CONTROL [SKYACTIV-X 2.0]
id0140hf188200
Outline
Block Diagram
ac30zn00001354
|
Operation
Ignition method
Timing chart
am3zzn00010098
|
Determination of Ignition Timing
|
Control zone |
Control condition |
Ignition method |
|---|---|---|
|
Engine start zone
|
Engine speed is less than 500 rpm
|
Engine starting
|
|
IR zone
|
During IR
|
IR ignition
|
|
Normal zone
|
During engine operation except for engine start zone and IR zone
|
Normal ignition (ignition timing is determined based on information from cylinder pressure sensor)
|
Ignition timing calculation method table
|
Contents
|
Calculation method or determination method for ignition timing, spark advance, and correction
|
Control zone
|
||
 |
 |
|||
|
Starting ignition
|
Determination based on engine coolant temperature
|
A
|
|
|
|
IR ignition
|
Determination based on engine coolant temperature
|
A
|
|
|
|
Normal ignition
|
Determination based on conditions inside cylinder (operation conditions of pressure, temperature, EGR, and each device and cylinder pressure sensor condition)
|
|
A
|
|
|
Correction
|
Engine coolant temperature spark advance correction
|
Purpose: Correction is performed because knocking and combustion period differ according to engine coolant temperature (temperature of wall inside cylinder).
|
|
B
|
|
Intake air temperature correction
|
Purpose: Correction is performed because SPCCI (Spark Controlled Compression Ignition) occurrence differs according to intake air temperature.
|
|
B
|
|
|
G/F correction (inside and outside)
|
Purpose: Correction is performed because knocking and combustion period differ according to EGR rate or fuel-air equivalence ratio.
|
|
B
|
|
|
Valve timing correction
|
Purpose: Correction is performed because combustion speed changes according to electric variable valve timing.
|
|
B
|
|
|
Swirl control valve position correction
|
Purpose: Correction is performed because combustion speed changes according to swirl control valve opening angle.
|
|
B
|
|