ELECTRIC VARIABLE VALVE TIMING CONTROL [SKYACTIV-X 2.0]
id0140hf318100
Outline
• The PCM determines the optimum valve timing for the engine operation conditions and sends the motor drive signals to the electric variable valve timing driver.
• With the adoption of electric drive on the exhaust side, variable control of valve timing coordinated with the intake side is performed unaffected by the engine conditions, achieving improved fuel economy and reduced pumping loss.
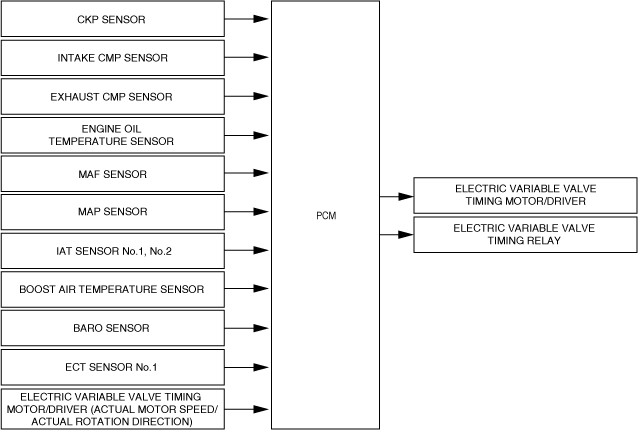
Block Diagram
Operation
Valve timing determination
-
• The PCM determines the optimum target Valve timing according to the engine operation conditions, and controls the output duty ratio to the electric variable valve timing driver so that the actual valve timing approaches close to the target valve timing.
-
Target valve timing
-
• The target valve timing is determined according to the engine speed, charging efficiency, and engine coolant temperature.
-
Actual valve timing
-
• The actual valve timing is calculated by adding a correction, which is based on the electric variable valve timing actuator signal value, to the value calculated by subtracting the cam maximum retard learning value from the standard valve timing.
• The standard valve timing is calculated based on the signals from the crankshaft position and camshaft position sensors.
-
Cam maximum retard learning value
-
• The cam maximum retard learning value is determined by the maximum retard indication output from the PCM and the standard valve timing when the standard valve timing is stabilized.
Output duty ratio determination
-
• The PCM divides the electric variable valve timing motor drive range modes according to the engine operation conditions, and determines the output duty ratio to the electric variable valve timing actuator in each mode.
|
Mode name
|
Control description
|
Control conditions
|
|
Feedback mode
|
• Continuously monitors the valve timing if it matches the target valve timing determined according to the engine operation condition, and controls the output duty ratio based on the result.
|
• Except for energization cut mode and phase holding mode
|
|
Energization cut mode
|
• If there is any malfunction in the electric variable valve timing driver, the valve timing is held at the maximum retard position to stabilize the engine speed.
|
• Electric variable valve timing driver malfunction
|
|
Phase holding mode
|
• To improve the startability, the phase of the electric variable valve timing actuator is held at the intermediate position after the engine is stopped.
|
• After the engine is stopped (Depending on the engine coolant temperature, operates after a certain period has elapsed from when the engine was stopped to suppress heating of the electrical variable valve timing motor.)
|