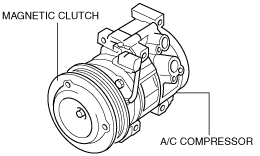
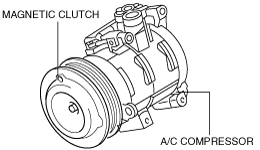
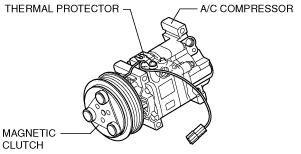
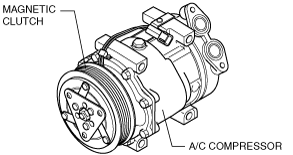
A/C COMPRESSOR CONSTRUCTION
id071100100600
• Consists of the following parts:
L5, L3 Turbo
LF, MZR 2.0 DISI i-stop
Z6, ZY
MZ-CD 1.6 (Y6) (EURO4 emission level)
MZ-CD 1.6 (Y6) (EURO5 emission level)
MZR-CD 2.2
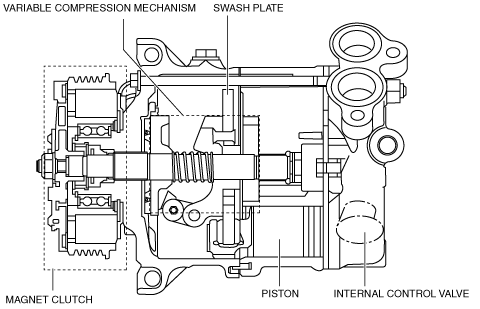
Variable Compressor (MZ-CD 1.6 (Y6))
• An A/C compressor for the MZ-CD 1.6 (Y6) has been adopted to the variable A/C compressor which changes the refrigerant pressure amount according to the refrigerant pressure conditions.
• When high cooling performance is needed, the piston operation level increases to enhance cooling performance. If the cooling performance is excessive, the piston operation level decreases and compressor load is reduced so that no surplus load is applied to the engine.
• The variable compressor consists of the following parts:
-
― Variable compression mechanism
― Magnet clutch
― Internal control valve
― Piston
― Swash plate
Improvement of cooling performance not needed (cooling performance exceeded)
-
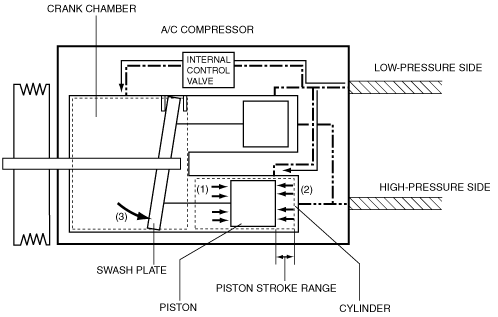
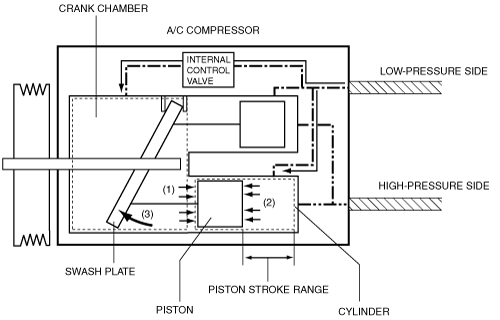
• If refrigerant pressure on the low-pressure side is high, refrigerant pressure applied to the crank chamber increases. Refrigerant pressure (1) is applied from the cylinder side in conjunction with the refrigerant pressure (2) applied to the piston from the crank chamber. The piston position is determined by taking the balance of each refrigerant pressure. If the refrigerant pressure is high, the piston position is away from the swash plate side. Therefore, the angle of the swash plate decreases in conjunction with the piston position (3). As a result, the A/C compressor output decreases because the piston stroke decreases.
• The internal control valve detects refrigerant pressure sent from the low-pressure side and controls refrigerant pressure sent to the crank chamber.
Improvement of cooling performance is needed (cooling performance insufficient)
-
• If refrigerant pressure on the low-pressure side is low, refrigerant pressure applied to the crank chamber decreases. Refrigerant pressure (1) is applied from the cylinder side in conjunction with the refrigerant pressure (2) applied to the piston from the crank chamber. The piston position is determined by taking the balance of each refrigerant pressure. If the refrigerant pressure is low, the piston position is close to the swash plate side. Therefore, the angle of the swash plate increases in conjunction with the piston position (3). As a result, the A/C compressor output increases because the piston stroke increases.
• The internal control valve detects refrigerant pressure sent from the low-pressure side and controls refrigerant pressure sent to the crank chamber.