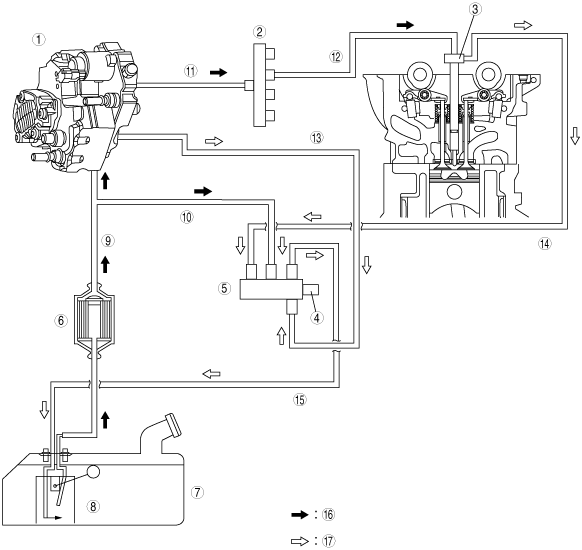
Here, the pressurized fuel is stored. Optimum fuel pressure is therefore always available at the injectors.
Injection timing and quantity are calculated by the PCM.
Taking the various input variables into consideration, the PCM actuates the solenoid valve‐controlled fuel injectors, which then inject the specified quantity of fuel into the respective cylinder.
The remaining fuel enters the fuel return via the fuel return hoses.
The fuel pressure sensor on the common rail provides the PCM with information on the current fuel pressure. Another parameter is the fuel temperature (not shown in the illustration). Using these parameters, the fuel metering valve regulates the fuel metering (by changing the cross‐section of the inlet channel to the high‐ pressure chambers) for the fuel pump, which ensures optimum fuel pressure for all operating conditions.
d3e114cw1501
|
|
1
|
Fuel pump
|
|
2
|
Common rail
|
|
3
|
Fuel injector
|
|
4
|
Fuel temperature sensor
|
|
5
|
Fuel return manifold
|
|
6
|
Fuel filter
|
|
7
|
Fuel tank
|
|
8
|
Fuel‐level sensor
|
|
9
|
Fuel feed
|
|
10
|
Outlet pipe for excess fuel delivered
|
|
11
|
High‐pressure fuel pipe (fuel pump side)
|
|
12
|
High‐pressure fuel pipe (fuel injector side)
|
|
13
|
Fuel return from fuel pump
|
|
14
|
Fuel return hose
|
|
15
|
Fuel return to fuel tank
|
|
16
|
Main fuel flow
|
|
17
|
Return fuel flow
|