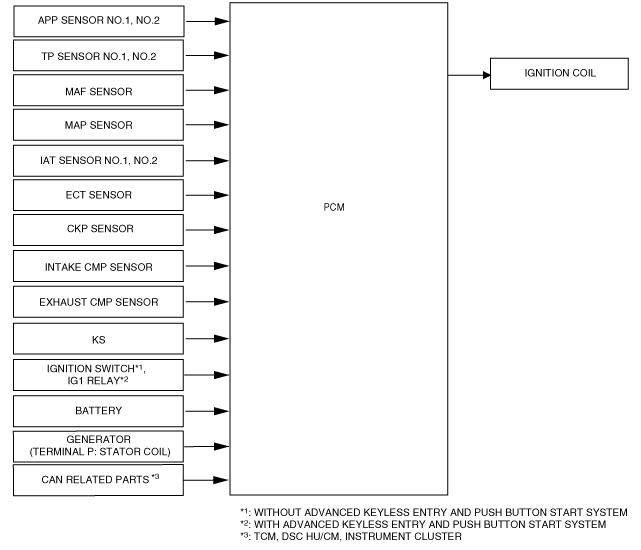
 |
am3zzn00003363
ELECTRONIC SPARK ADVANCE CONTROL [SKYACTIV-G 2.0]
id0140f4188200
Outline
Block Diagram
am3zzn00003363
|
Operation
Ignition method
|
Ignition method |
Ignition timing |
Ignition coil energization period |
|---|---|---|
|
Starting ignition
|
Determination based on engine coolant temperature
|
• Energization time to igniter (ignition coil energization time) is determined according to battery voltage
• Cylinder independent ignition
|
|
Cycle estimated ignition
|
Ignition at timing appropriate to engine operation conditions based on input signals
|
Timing chart
am3zzn00003421
|
Determination of Ignition Timing
am3uun00001983
|
|
Control zone |
Control condition |
Ignition method |
|---|---|---|
|
Engine start
|
Engine speed is less than 500 rpm
|
Engine starting
|
|
Idle zone
|
Accelerator pedal not depressed
|
(Cycle estimated ignition) (Determines ignition timing adding each correction to idle spark advance)
|
|
Normal zone
|
Engine operation except start and idling zones
|
(Cycle estimated ignition) (Determines ignition timing adding each correction to basic spark advance)
|
Ignition timing calculation method table
|
Contents
|
Calculation method or determination method for ignition timing, spark advance, and correction
|
Control zone
|
|||
 |
 |
 |
|||
|
Starting ignition
|
Determination based on engine coolant temperature
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
Cycle estimated ignition
|
Idle spark advance
|
Set value according to target speed and charging efficiency*
|
|
A
|
|
|
Basic spark advance
|
Set value according to engine speed and charging efficiency*
|
|
|
A
|
|
|
Correction
|
Engine coolant temperature spark advance correction
|
Purpose: Ensures combustion stability when engine coolant temperature is low
According to engine coolant temperature
• High charging efficiency*, low engine coolant temperature→large correction
|
|
B
|
B
|
|
Warm-up promotion spark retard correction
|
Purpose: Activates the catalytic converter earlier
Approx. 50 s after engine start
• According to engine coolant temperature→correction
|
|
B
|
|
|
|
Feedback correction
|
Purpose: Ensures idling stability
While idling (inhibited during test mode)
• Large difference between actual engine speed and target engine speed→large correction
• Small difference between actual engine speed and target engine speed→small correction
|
|
B
|
|
|
|
Retard correction
|
Purpose: Reduces shift shock during down shifting
According to torque reduction request signal from TCM and DSC HU/CM
• Large torque reduction request during shifting→large correction
|
|
|
B
|
|
|
Deceleration fuel cut recovery retard correction
|
Purpose: Reduces shock during recovery from deceleration fuel cut
Recovery from deceleration fuel cut
• Difference between turbine speed and engine speed is larger→large correction
|
|
B
|
B
|
|
|
Acceleration spark retard correction
|
Purpose: Prevents knocking and shock during sudden acceleration
Acceleration when charging efficiency* volume increase (acceleration amount) is given value or more
• Large acceleration amount→large correction
|
|
|
B
|
|
|
Acceleration from standstill spark retard correction
|
Purpose: To prevent shock when the vehicle accelerates from a standstill
When vehicle accelerates from a standstill
• According to engine speed, throttle valve opening angle, accelerator, gear, clutch, engine coolant temperature and intake air temperature→correction
|
|
|
B
|
|
|
Knocking spark retard correction
|
Purpose: Knocking suppression
When knocking is detected while driving under a load
• Large amount of knocking→large correction
|
|
|
B
|
|
|
Valve timing correction
|
Purpose: Ensures combustion stability
When phase difference changes due to electric variable valve timing control and variable valve timing control
• Correction according to change in phase difference
|
|
|
B
|
|