COMBINED SENSOR CONSTRUCTION/OPERATION
id041500101900
• The output voltage characteristic for the combined sensor is 2.5 V when the vehicle is standing still, and changes accordingly as yaw rate, lateral G and forward G is formed.
• Yaw rate is formed when the sensor detects a Coriolis force created by, and in proportion to, the rotation speed of a rotating tuning fork.
• Lateral G is formed when the sensor detects an inertial force created by, and in proportion to, a G force acting on a silicon detection component.
• Forward-G is formed when the sensor detects an inertial force created by, and in proportion to, a G- force acting on a silicon detection component.
• The drive train of 4WD vehicles delivers driving force to all four wheels, and due to this interlocking, the speed of all wheels during braking is the same. When driving on road surfaces with especially low mu (friction coefficient), it is difficult to estimate the vehicle speed based on the wheel speed, and DSC braking becomes unreliable. (For 2WD vehicles, the front and rear wheels are independent, so it is possible to accurately estimate the vehicle speed by measuring the difference between the rotation speeds of the front and rear tires.) A forward-G sensor has been installed to overcome this situation. When braking, the change in G-force is detected, and the road surface mu is judged (low mu, high mu), enabling a correction of the vehicle speed estimation.
-
Note
-
• The Coriolis force: When an object on a rotating disc attempts to move toward the disc's center, force is produced at a right angle to the object's intended path of travel. This results in the object's direction of movement being unchanged from its original point of departure, and it not reaching the center. When looking at this effect from outside the disc, it appears as force deflecting the object away from the center. This appearance of force is called Coriolis force, and the object's actual direction of advance takes a straight course.
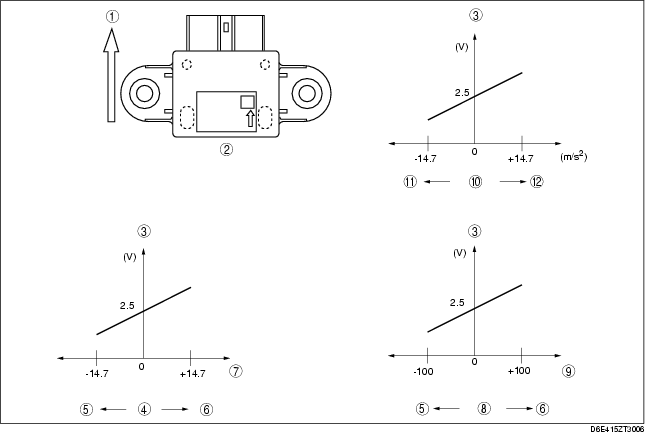
.
|
1
|
Front of vehicle
|
|
2
|
External view
|
|
3
|
Output voltage characteristic
|
|
4
|
Lateral-G
|
|
5
|
Left cornering
|
|
6
|
Right cornering
|
|
7
|
Acceleration (m/s2)
|
|
8
|
Output voltage characteristic
|
|
8
|
Yaw rate
|
|
9
|
Yaw rate (deg/s)
|
|
10
|
Forward-G
|
|
11
|
Deceleration
|
|
12
|
Acceleration
|

