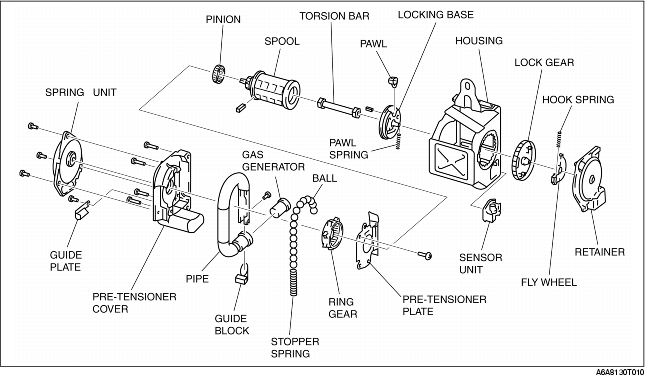

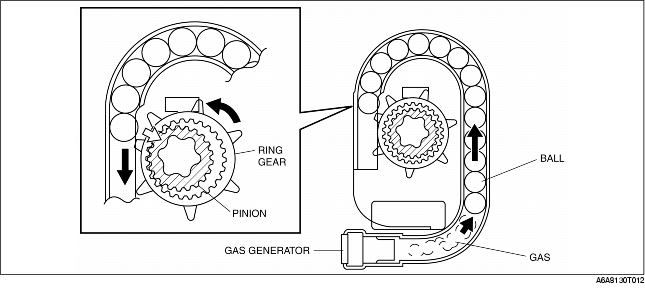
1. When the pre-tensioner seat belt system receives an operation signal from the SAS control module, gas is produced from each generator forcing up the balls in the tube.
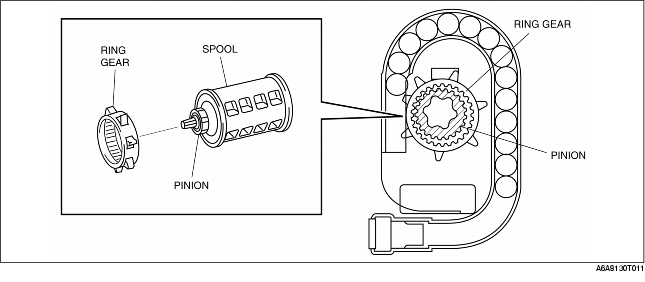
2. The balls shift, pushing the ring gear toward the pinion. Due to this, the ring gear and pinion are engaged.
3. The ball shifting makes the ring gear rotate. The pinion, coupled with the rotation of the ring gear, rotates the spool in the direction of retraction. Thus the belt webbing is tightened.
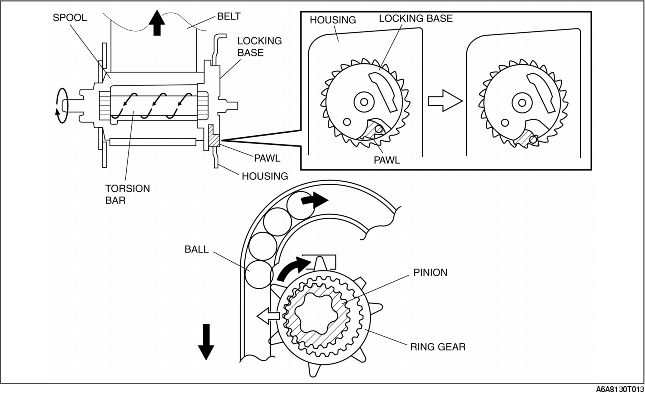
1. Directly after the activation of the pre-tensioner seat belt system and the application of a load to the seat belt in the direction of withdrawal, the ELR lock mechanism operates and the pawl engages the housing gear.
2. When a larger than specified load is applied to the seat belt with the locking base locked by the pawl, the torsion bar twists. Thus the spool rotates and the belt webbing is withdrawn.
3. Because the spool rotates in the direction of withdrawal, the ring gear pushes the balls back and the pinion is disengaged from the ring gear.