 |
am6zzn00003260
AIM OF DEVELOPMENT
id000000100100
Product Concept
Vehicle Outline
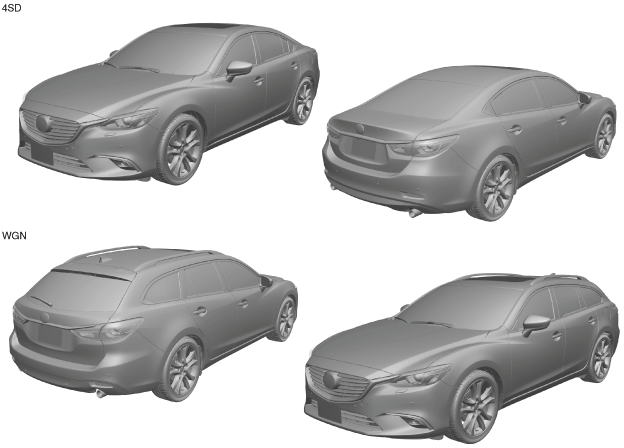
Exterior design
External view
am6zzn00003260
|
Interior design
am6zzn00003261
|
Engine
Suspension
ac5wzn00001047
|
2WD
ac5uun00000310
|
4WD
ac5uun00000311
|
Driveline/axle
Brakes
Vehicle front side (L.H.D.)
am6zzn00003859
|
Vehicle front side (R.H.D.)
am6zzn00003860
|
Vehicle rear side
am6zzn00003861
|
Vehicle front side (L.H.D.)
am6zzn00003208
|
Vehicle front side (R.H.D.)
am6zzn00003209
|
Vehicle rear side
am6zzn00003210
|
Transaxle
ac5wzn00001054
|
ac5wzn00001738
|
ac5wzn00001055
|
ac5jjn00001299
|
Steering
L.H.D. (Without Lane-Keep Assist System)
am6zzn00003216
|
L.H.D. (With Lane-Keep Assist System)
am6zzn00003217
|
R.H.D. (Without Lane-Keep Assist System)
am6zzn00003218
|
R.H.D. (With Lane-Keep Assist System)
am6zzn00003219
|
Safety
Driver's support