ELECTRONIC SPARK ADVANCE (ESA) OPERATION [13B-MSP]
id0140g1103100
Ignition Method
• The PCM controls fixed ignition and regular ignition according to the engine operation conditions.
|
Ignition Method
|
Ignition timing
|
|
Fixed ignition
|
Ignition fixed at BTDC 5°
|
|
Regular ignition
|
Appropriate ignition for engine operation conditions based on input signals.
|
Determination of Ignition Timing
Control Zone Divisions
• The PCM divides the full range of ignition control into control zones and determines the ignition timing from each control zone according to engine speed and throttle valve opening angle to perform optimum ignition control at the full range of engine operating conditions.
|
Ignition Method
|
Zone
|
Condition
|
Ignition timing
|
|
Fixed ignition
|
Start zone
|
Engine speed 500 rpm or less
|
Fixed ignition
|
|
Regular ignition
|
Idle zone
|
When the AP is fully closed (during idle).
|
Determined by addition of each type of correction to the basic spark advance.
|
|
Regular zone
|
During engine operation other than start zone and idle zone
|
Determined by addition of each type of correction to the basic spark advance.
|
Fixed Ignition
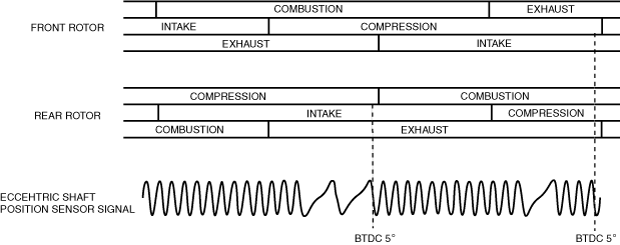
• At engine start, fixed ignition is performed at BTDC 5° until the engine speed reaches 500 rpm or more, due to ignition timing control difficulty from changes such as low battery positive voltage from start operation and fluctuations in engine speed.
Regular Ignition
• The PCM determines the optimum final ignition timing, adding each type of spark advance correction to the base spark advance, ECT spark advance correction, and the IAT spark advance correction.
Basic spark advance
-
• The basic spark advance becomes the basis for the ignition timing control.
• The basic spark advance amount is determined by the engine speed, charging efficiency and the ECT.
ECT spark advance correction
-
• Corrects other than during idling.
• Stabilizes combustion by correction of ignition timing in consideration of friction loss when the engine is at a low temperature.
• The correction amount is determined by the ECT and charging efficiency, and increases as the ECT decreases.
IAT spark advance correction
-
• Corrects ignition timing according to the IAT.
• The correction amount is determined by the IAT, idling condition and charging efficiency, and increases as the IAT decreases.
Types of spark advance correction
-
• Spark advance correction is as follows:
Knock feedback correction
-
• When knocking is detected, ignition timing is retarded, stabilizing the combustion condition.
Idling stabilization correction
-
• Correction stabilizes engine speed during idling. The correction amount is determined by the actual engine speed and the average engine speed.
Fast idle correction
-
• At cold-engine start, the correction is performed to accelerate secondary air response (reburn), decrease unburnt gas, and rapidly activate the catalytic converter.
Low temperature correction
-
• Performs spark advance correction of ignition timing to stabilize combustion during low temperature. Low temperature correction performs advance of ignition timing when ECT is less than 90°C {194°F} and the AP is depressed, and is determined by ECT, charging efficiency and engine speed.
Acceleration correction
-
• Performs retard correction of ignition timing to prevent knocking at acceleration from a standstill. Correction amount is determined by the amount of throttle valve change, the charging efficiency and the ECT.
Fuel cut recovery correction
-
• Performs retard correction of ignition timing during recovery from deceleration fuel cut to prevent shock during fuel cut recovery. Correction amount is determined by idling condition, A/C condition and engine speed.
Surging correction
-
• Performs spark retard correction due to acceleration vibration to stabilize acceleration. Correction amount is determined by the engine speed and the amount of engine speed change.
Acceleration shock correction
-
• Gradually restores ignition timing after it is retarded for a fixed period of time to inhibit shock during acceleration.
A/C off correction
-
• The retard correction is performed to prevent engine speed fluctuation due to load decrease when the A/C switch is off. The correction amount is determined by the engine speed and the charging efficiency, and decreases as the engine speed and the charging efficiency are high.
Traction correction
-
• The spark timing is retarded following a torque down request from the DSC HU/CM and TCM (AT), reducing engine torque.