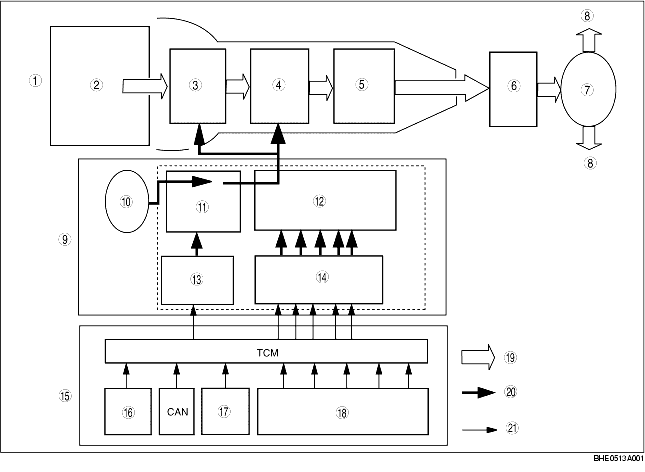
• The outline of the electronically-controlled automatic transmission is classified into three systems: the powertrain system (includes the torque converter mechanism), the hydraulic control system, and the electronic control system.
• Driving force from the engine is transmitted through the torque converter to the transmission.
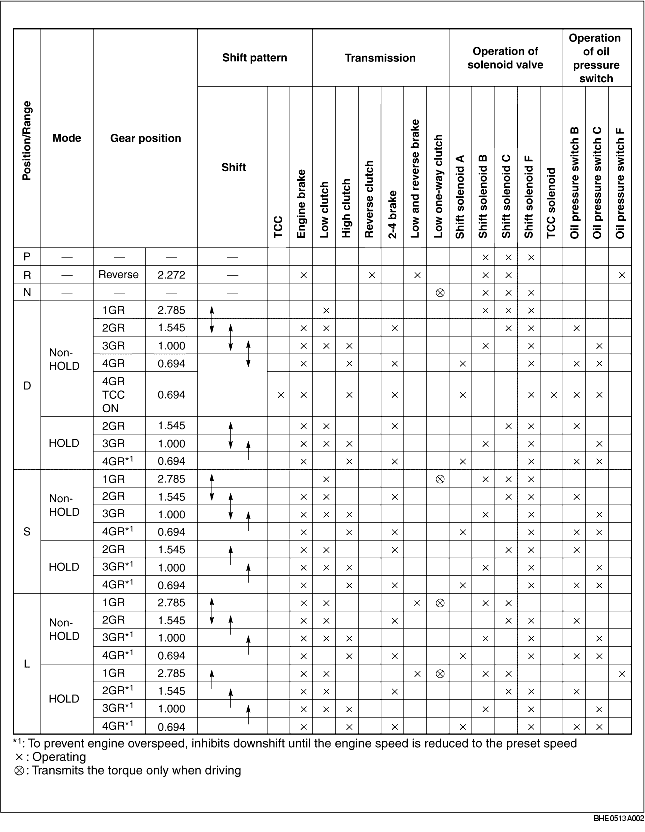
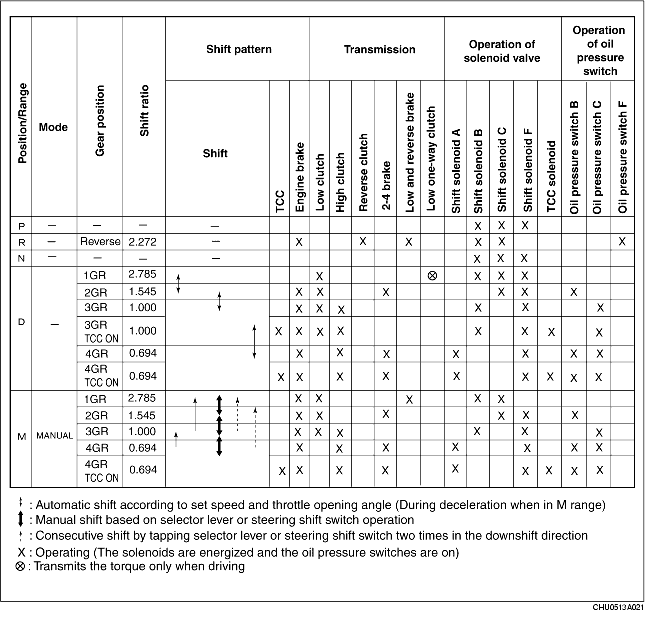
• When the clutch and brakes are engaged by clutch pressure from the control valve, the planetary gear unit switches between fixed and input, and thus transmitted driving force is converted to optimum driving force.
• The converted driving force is transmitted to the propeller shaft, the differential, and the tires.
• The solenoids operate, according to the signals from the TCM, to switch to high or low line pressure (depending on driving conditions) and regulate the clutch pressure.
• The on/off pressure control solenoid switches line pressure between high and low, duty cycle shift solenoids regulate clutch pressure, and duty cycle TCC solenoids control TCC.
• The TCM sends signals that suit current driving conditions to the solenoids of the hydraulic control system, according to input signals from sensors and switches, and shifts gears.