GENERATOR OUTPUT CONTROL OPERATION [L3 R.H.D.]
BUE014000000N48
Determination of field coil excitation time
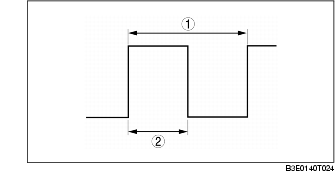
|
1
|
Single cycle
|
|
2
|
Energization time
|
• By sending a duty signal to the power transistor built into the generator, the PCM increases and decreases the field coil excitation current.
• The duty signal changes the field coil energization current by varying the power transistor excitation time during a single cycle within a specified frequency range. For example, when the battery positive voltage drops, the energization time of the duty signal sent to the power transistor is longer, increasing the field coil excitation current.
Control
• To maintain optimum battery voltage, the PCM calculates the target excitation current based on the targeted generator current (target generated current) and the generator rotation speed at the time.
• The generator rotation speed is calculated from the generator pulley and crankshaft pulley ratios, and the engine speed.
• The PCM compares the target battery positive voltage (regulating voltage) calculated from the intake air temperature and engine speed with the current battery positive voltage and, based on this difference, calculates the required generator current.
• When an electrical load is applied, the target rotation speed increases while idling because the battery positive voltage decreases due to the increased power consumption.