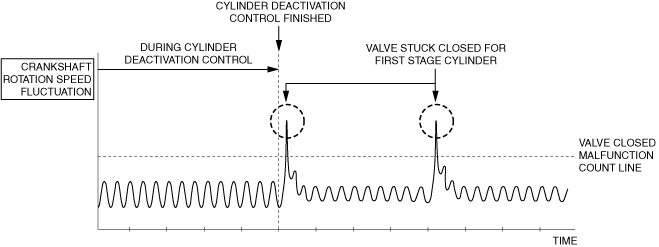
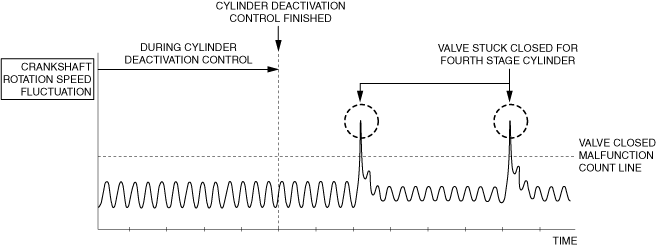
|
1
|
PURPOSE: DETERMINE INTEGRITY OF SPARK PLUG
• Inspect the spark plug.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Replace the spark plug, then go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
2
|
PURPOSE: DETERMINE INTEGRITY OF IGNITION COIL
• Inspect the ignition coil.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Replace the ignition coil/ion sensor, then go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
3
|
PURPOSE: DETERMINE INTEGRITY OF OCV FOR No.1 CYLINDER DEACTIVATION
• Inspect the OCV for No.1 cylinder deactivation.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Replace the OCV for No.1 cylinder deactivation, then go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
4
|
PURPOSE: DETERMINE INTEGRITY OF OCV FOR No.4 CYLINDER DEACTIVATION
• Inspect the OCV for No.4 cylinder deactivation.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Replace the OCV for No.4 cylinder deactivation, then go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
5
|
PURPOSE: DETERMINE INTEGRITY OF SWITCHABLE HLA
• Inspect the Switchable HLA.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Replace the Switchable HLA, then go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
6
|
PURPOSE: DETERMINE INTEGRITY OF ENGINE OIL SOLENOID VALVE
• Inspect the engine oil solenoid valve.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Replace the engine oil solenoid valve, then go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
7
|
PURPOSE: DETERMINE INTEGRITY OF FUEL INJECTOR
• Inspect the fuel injector.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Replace the fuel injector, then go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
8
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY IF MALFUNCTION RELATED TO INTAKE-AIR SYSTEM IS CAUSE OF VALVE BEING STUCK CLOSED
• Visually inspect for loose, cracked or damaged hoses on intake air system.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning part according to the inspection results, then go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
9
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY IF POOR DRIVE BELT ASSEMBLY IS CAUSE OF VALVE BEING STUCK CLOSED
• Verify the condition of the drive belt assembly.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Assemble drive belt correctly, then go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
10
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY IF FOREIGN MATTER ON DRIVE BELT IS CAUSE OF VALVE BEING STUCK CLOSED
• Verify if oil is on the drive belt.
• Is there foreign matter on the drive belt?
|
Yes
|
Remove the foreign matter on the drive belt, then go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
11
|
PURPOSE: DETERMINE INTEGRITY OF DRIVE BELT AUTO TENSIONER
• Inspect the drive belt auto tensioner.
• Is there any malfunction?
|
Yes
|
Replace the drive belt auto tensioner, then go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
12
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY IF MALFUNCTION RELATED TO ENGINE COMPRESSION IS CAUSE OF VALVE BEING STUCK CLOSED
• Inspect the engine compression.
• Are compression pressures within specification?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Replace or overhaul the engine, then go to Step 15.
|
|
13
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY IF MALFUNCTION RELATED TO SEALING OF ENGINE UNIT (COMBUSTION CHAMBER AND ENGINE COOLANT PASSAGE) IS CAUSE OF MISFIRE
• Perform the “ENGINE COOLANT LEAKAGE INSPECTION”.
• Does the radiator cap tester needle drop even though there is no engine coolant leakage from the radiator or the hoses?
|
Yes
|
Engine coolant leakage from the engine (between the combustion chamber and the engine coolant passage) may have occurred.
• Verify the conditions of the gasket and the cylinder head.
-
― If there is any malfunction:
-
• Repair or replace the malfunctioning part according to the inspection results, then go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
14
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT FOR MALFUNCTION DUE TO INTERNAL ENGINE WEAR, DAMAGE
• Inspect for the following engine internal parts:
-
― Cylinder
― Piston ring
― Intake valve
― Exhaust valve
― Such as cylinder head gasket
• Are all items normal?
|
Yes
|
Engine internal parts are normal.
• Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning part according to the inspection results, then go to the next step.
|
|
15
|
PURPOSE: VERIFICATION OF VEHICLE REPAIR COMPLETION
• Always reconnect all disconnected connectors.
• Clear the DTC from the PCM memory using the M-MDS.
• Start the engine and warm it up completely.
-
Caution
-
• While performing this step, always operate the vehicle in a safe and lawful manner.
• When the M-MDS is used to observe monitor system status while driving, be sure to have another technician with you, or record the data in the M-MDS using the PID/DATA MONITOR AND RECORD capturing function and inspect later.
• Drive the vehicle under the snapshot data condition.
• Perform the DTC Reading Procedure.
• Is the same DTC present?
|
Yes
|
Repeat the inspection from Step 1.
• If the malfunction recurs, replace the PCM.
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
16
|
VERIFY AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE
• Perform the “AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE”.
• Are any DTCs present?
|
Yes
|
Go to the applicable DTC inspection.
|
|
No
|
DTC troubleshooting completed.
|