ELECTRIC POWER STEERING (EPS) CONTROL MODULE [(E)]
id0613002455x2
Purpose/ Function
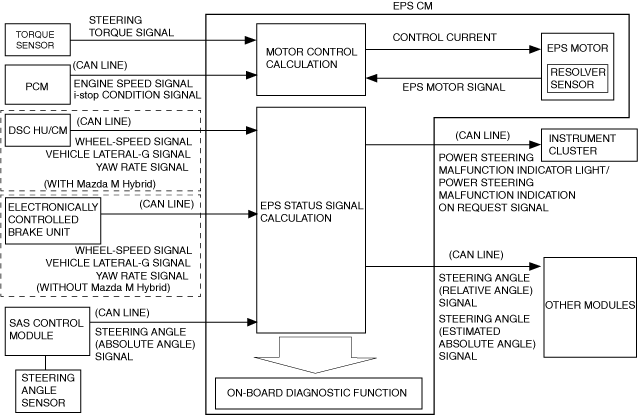
• The EPS CM calculates optimum assist force based on the steering torque signal from the torque sensor,the vehicle speed signal from the DSC HU/CM(without Mazda M Hybrid system), electronically controlled brake unit(with Mazda M Hybrid system), engine speed signal from the PCM, and EPS motor position information from the EPS motor, and outputs electric current to drive the EPS motor.
• The following steering angle signals are output via CAN communication.
-
― Steering angle (relative angle) signal
-
• Set the steering position to when the ignition is switched ON (engine off or on) to output the steering angle when steering from that position.
― Steering angle (estimated absolute angle) signal
-
• The EPS CM outputs the calculated steering angle value to the CAN as a steering angle (estimated absolute angle) signal for other systems requiring steering angle information.
-
Note
-
• The steering angle sensor signal is not used for the steering angle (estimated absolute angle) signal calculation.
• After the steering angle neutral position auto learning is completed, the EPS CM outputs an EPS status signal, which is calculated by EPS CM itself, through the CAN communication.
• The EPS CM controls the following functions:
Function Table
|
Control item
|
Function
|
|
EPS motor current control
|
• Normal control
-
― Calculates the proper assist current based on the steering torque, and the vehicle and engine speeds, and outputs a target current to the EPS motor.
• System overheating protection control
-
― Monitors the temperature of the motherboard in the EPS CM and controls the motor current gradually to prevent overheating of the system.
• EPS motor backup control
-
― Even if a phase 1 open circuit malfunction in the EPS motor occurs, output current to the EPS motor is controlled so that steering assist is maintained.
• Torque sensor backup control
-
― Even if an error occurs in the torque sensor signal, the torque sensor backup control performs control to maintain steering assist to the extent possible.
• Resolver sensor backup control
-
― Even if an open circuit malfunction occurs in the resolver sensor, the resolver sensor backup control performs control to maintain steering assist to the extent possible.
• EPS i-stop control
-
― Control current to the EPS motor is increased or decreased according to the operation status of the i-stop system.
• Current sensor backup control
-
― Even if a current sensor malfunction occurs, output current to the EPS motor is controlled so that steering assist is maintained.
• IG backup control
-
― Even if an IG signal error occurs, output current to the EPS motor is controlled so that steering assist is maintained. However, the assist while the vehicle is stopped is ended.
|
|
On-board diagnostic function
|
• The main part of the system control includes the self-diagnosis function. In case a malfunction occurs, the power steering malfunction indication/master warning light illuminates to alert the driver, and a DTC is stored in the EPS CM at the same time.
• As a result of the on-board diagnosis, when a malfunction is determined, system control is suspended or limited to assure safety while driving.
|
|
CAN communication function
|
• Outputs the EPS status signal and the power steering malfunction indication illuminates on request via CAN lines.
• Outputs the steering angle (absolute angle) signal, steering angle (relative angle) signal and steering angle (estimated absolute angle) signal.
|
|
Automatic configuration function
|
• When the ignition is switched to ON or the engine is started after the EPS CM have been replaced, the EPS CM reads data from the instrument cluster via CAN communication to perform automatic configuration.
|
|
Steering wheel angle neutral position automatic learning function
|
• When the ignition is switched from OFF to ON (engine on) and the vehicle is driven normally, the steering wheel angle neutral position is learned automatically based on the wheel speed signal, lateral-G signal, and yaw rate signal.
|
Construction
• The EPS CM is installed to the steering column and integrated with the EPS motor.
• For vehicles equipped with a system requiring steering angle information directly after the vehicle starts to be driven, a steering angle sensor is equipped.
Block Diagram
Operation
• The EPS CM calculates the required assist torque based on the steering torque signal from the torque sensor. When the vehicle starts to be driven, the required assist torque is calculated based on the vehicle speed signal sent from the DSC HU/CM(without Mazda M Hybrid system) or electronically controlled brake unit(with Mazda M Hybrid system) via CAN in addition to the steering torque signal.
• The EPS system control uses the steering angle (estimated absolute angle) signal.
Ignition is switched ON (engine off or on)
-
― The EPS CM regards the steering position when the ignition is switched ON (engine off or on) as , and outputs the steering angle value steered from that position as a steering angle (relative angle) signal.
Vehicle driving
-
― When the vehicle starts to be driven, the EPS CM performs steering wheel angle neutral position determination based on the following signals:
-
• Wheel speed signal: Determines straight-driving if there is no rotation speed difference between the left/right wheels.
• Lateral-G signal: Determines straight-driving if lateral-G is not produced.
• Yaw rate signal: Determines straight-driving if yaw momentum is not produced.
― If the EPS CM completes steering wheel angle neutral position determination, the steering angle neutral position is set. The EPS CM regards the steering wheel angle neutral position as , calculates the estimated absolute steering angle, and outputs the steering angle (estimated absolute angle) signal to CAN.
Ignition is switched off
-
― The steering wheel angle neutral position is cleared when 1 min or more has elapsed after the ignition is switched off.
• When the following controls are performed, the EPS CM stores a DTC and turns on the electric power steering warning light/electric power steering warning indication.
-
― EPS motor backup control
― Resolver sensor backup control
― IG backup control
― Current sensor backup control
-
• For details on the DTCs with which the electric power steering warning light/electric power steering warning indication turns on, refer to the workshop manual.
EPS Motor Current Control
-
Normal control
-
• The optimum assist current is calculated based on the steering force signal from the torque sensor and the vehicle speed signal from the DSC HU/CM(without Mazda M Hybrid system) or electronically controlled brake unit(with Mazda M Hybrid system), and then the control current is output to the EPS motor.
-
System overheating protection control
-
• The system overheating protection control lowers the current output to the EPS motor if the steering mechanism is turned from lock to lock continuously or the steering rack turning limit is reached repeatedly.
-
Note
-
• During system overheating protection control, the assist force will feel weaker due to a decrease in the control current. This is normal for the EPS CM to prevent the EPS motor from burning or seizure, and it does not indicate a malfunction.
• While the assist force weakens during this period of time, steering operation can be performed.
• The system overheating protection control has high and low steps, and it can verify current conditions and the history using the PID/data monitor function and snap shot data.
-
― System overheating protection control (high): Motor output is 80 % or less (reference)
― System overheating protection control (low): Motor output is 50 % or less (reference)
• The current output returns to normal if the temperature in the system decreases to the normal operation temperature.
-
EPS motor backup control
-
• Even if an open circuit malfunction occurs in 1 out of the 3 phases in the EPS motor line, the EPS motor backup control performs control to maintain steering assist.
• If the EPS CM detects a phase 1 open circuit malfunction in the EPS motor, the EPS CM controls output current to the EPS motor using a calculation method different than during normal EPS CM control. As a result, even with a phase 1 open circuit malfunction, the steering assist can be maintained.
-
Note
-
• If the steering wheel is operated during EPS motor backup control, the steering wheel operation may feel heavier (resistance).
-
Torque sensor backup control
-
• Even if an error is detected in the torque sensor signal, the torque sensor backup control performs control to maintain steering assist.
• If the EPS CM detects a torque sensor signal error, the EPS CM controls output current to the EPS motor using a calculation method different from that during normal EPS CM control, and maintains steering assist.
-
Note
-
• If the steering wheel is operated during torque sensor backup control, normal assist force may not be generated.
-
Resolver sensor backup control
-
• Even if an open circuit malfunction occurs in the resolver sensor, the resolver sensor backup control performs control to maintain steering assist.
• If the EPS CM detects an open circuit malfunction in the resolver sensor, the EPS CM controls output current to the EPS motor using a calculation method different from that during normal EPS CM control. As a result, even with an open circuit in the resolver sensor, the steering assist can be maintained.
-
IG backup control
-
• Even if an error is detected in the IG signal, the IG backup control performs control to maintain steering assist.
• If the EPS CM detects an IG signal error, the EPS CM controls output current to the EPS motor using a calculation method different from that during normal EPS CM control.As a result, even if an error occurs with the IG signal, the steering assist can be maintained. When the vehicle speed is 0 km/h, assistance is stopped.
-
Current sensor backup control
-
• Even if an open circuit malfunction occurs in the current sensor, the current sensor backup control performs control to maintain steering assist.
• If the EPS CM detects an open circuit malfunction in the current sensor, the EPS CM controls output current to the EPS motor using a calculation method different from? that during normal EPS CM control.As a result, even with an open circuit malfunction in the current sensor, the steering assist can be maintained.
-
EPS i-stop control
-
• If it is detected that the engine is stopped by the i-stop control based on the i-stop condition signal from the PCM, the EPS motor control current is stopped.
• If it is detected that the engine is restarted by the i-stop control, the EPS motor control current is increased and the system returns to normal control.
• If the steering wheel is operated during EPS i-stop control, assist is performed (normal control) according to that steering.
• If a malfunction is detected in the i-stop condition signal from the PCM, EPS i-stop control is not operated, and normal control is performed.
• Depending on the vehicle condition, the EPS CM may continue assistance even after the engine is stopped.