 |
MECHANICAL SYSTEM TEST [FN4A-EL]
id0517a1802100
Mechanical System Test Preparation
1. Engage the parking brake and use wheel chocks at the front and rear of the wheels.
2. Inspect the engine coolant level. (See COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE WARNINGS [ZJ, ZY, Z6].) (See COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE WARNINGS [LF, L3].) (See ENGINE COOLANT LEVEL INSPECTION [ZJ, ZY, Z6].) (See ENGINE COOLANT LEVEL INSPECTION [LF, L3].)
3. Inspect the engine oil level. (See ENGINE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION [ZJ, ZY, Z6].) (See ENGINE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION [LF, L3].)
4. Inspect the ATF level. (See AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID (ATF) INSPECTION [FN4A-EL].)
5. Inspect the ignition timing. (See ENGINE TUNE-UP [ZJ, ZY, Z6].) (See ENGINE TUNE-UP [LF, L3].)
6. Inspect the idle speed. (See ENGINE TUNE-UP [ZJ, ZY, Z6].) (See ENGINE TUNE-UP [LF, L3].)
Line Pressure Test
1. Perform mechanical system test preparation. (See Mechanical System Test Preparation.)
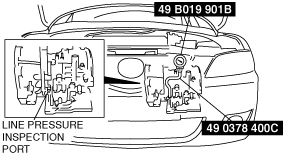
2. Connect the SSTs (49 0378 400C) to the line pressure inspection port and replace the gauge of the SST (49 0378 400C) with the SST (49 B019 901B).
am3zzw00001195
|
3. Start the engine and warm it up until the ATF reaches 60—70 °C {140—158 °F}.
4. Shift the selector lever to the D range.
5. Read the line pressure while the engine is idling for the D range.
6. Read the line pressure while the engine is idling for the R position and M (1GR, 2GR) range in the same manner as in Steps 4—5.
7. Stop the engine, then replace the SST (49 B019 901B) with the gauge of the SST (49 0378 400C).
8. Start the engine.
9. Firmly depress the brake pedal with the left foot.
10. Shift the selector lever to the D range.
11. Gradually depress the accelerator pedal with the right foot.
12. When the engine speed no longer increases, quickly read the line pressure and release the accelerator pedal.
13. Shift the selector lever to the N position and idle the engine for 1 min or more to cool the ATF.
14. Read the line pressure at the engine stall speed for the M (1GR, 2GR) range and R position in the same manner as in Steps 9—13.
Line pressure specification
|
Position/range |
Line pressure (kPa {kgf/cm2, psi}) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Z6 |
ZY |
LF (Except Israel specs.) |
LF (Israel specs.) |
||
|
D,
M (1GR, 2GR)
|
Idle
|
330—470
{3.4—4.7, 48—68}
|
|||
|
Stall
|
1,080—1,270
{11.1—12.9, 157—184}
|
970—1,130
{9.9—11.5, 141—163}
|
1,160—1,320
{11.9—13.4, 169—191}
|
||
|
R
|
Idle
|
490—710
{5.0—7.2, 72—102}
|
|||
|
Stall
|
1,500—1,720
{15.3—17.5, 218—249}
|
1,580—1,880
{16.2—19.1, 230—272}
|
1,680—2,020
{17.2—20.5, 244—292}
|
1,730—2,070
{17.7—21.1, 251—300}
|
|
15. Remove the SSTs.
16. Install a new square head plug in the inspection port.
Evaluation of line pressure test
|
Condition |
Possible cause |
|---|---|
|
Low pressure in all position/ranges
|
• Worn oil pump
• Oil leaking from oil pump, control valve body, and/or transaxle case
• Pressure regulator valve stuck
• Pressure control solenoid malfunction
• Solenoid reducing valve stuck
|
|
Low pressure in D, M (1GR, 2GR) ranges
|
• Oil leaking from forward clutch hydraulic circuit
|
|
Low pressure in M (2GR) range
|
• Oil leaking from 2-4 brake band hydraulic circuit
|
|
Low pressure in M (1GR) range, R position
|
• Oil leaking from low and reverse brake hydraulic circuit
|
|
Low pressure in R position
|
• Oil leaking from reverse clutch hydraulic circuit
|
|
Higher pressure in all position/ranges
|
• Pressure control solenoid malfunction and/or open harness
• Pressure regulator valve stuck
• TCM malfunction
|
Stall Test
1. Perform mechanical system test preparation. (See Mechanical System Test Preparation.)
2. Start the engine.
3. Firmly depress the brake pedal with the left foot.
4. Shift the selector lever to the D range.
5. Gently depress the accelerator pedal with the right foot.
6. When the engine speed no longer increases, quickly read the engine speed and release the accelerator pedal.
7. Shift the selector lever to the N position and idle the engine for 1 min or more to cool the ATF.
8. Perform a stall test of the M range and R position in the same manner as in Steps 3—7.
9. Turn off the engine.
Engine stall speed
|
Position/range |
Engine stall speed (rpm) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Z6 |
ZY |
LF (Except Israel specs.) |
LF (Israel specs.) |
|
|
D, M (1GR, 2GR)
|
2,100—2,700
|
2,200—2,800
|
2,300—2,900
|
|
|
R
|
||||
Evaluation of stall test
|
Condition |
Possible cause |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Above specification
|
In all position/ranges
|
Insufficient line pressure
|
• Worn oil pump
|
|
• Oil leaking from oil pump, control valve, and/or transaxle case
|
|||
|
• Pressure regulator valve sticking
|
|||
|
• Converter relief valve sticking
|
|||
|
• Pressure control solenoid malfunction
|
|||
|
In D, M (1GR, 2GR) ranges
|
• Forward clutch slipping
|
||
|
In D range
|
• One-way clutch malfunction
|
||
|
In D, M (2GR) ranges
|
• 2-4 brake band slipping
• One-way clutch malfunction
|
||
|
In D, M (1GR) ranges
|
• Low and reverse brake slipping
• One-way clutch malfunction
|
||
|
In R position
|
• Low and reverse brake slipping
• Reverse clutch slipping
• Perform road test to determine whether problem is in low and reverse brake or reverse clutch
|
||
|
Below specification
|
• Engine lack of power
|
||
Time Lag Test
1. Perform mechanical system test preparation. (See Mechanical System Test Preparation.)
2. Start the engine.
3. Warm up the engine until the ATF temperature reaches 60—70°C {140—158°F}.
4. Shift the selector lever from the N position to D range.
5. Use a stopwatch to measure the time it takes from shifting until shock is felt. Take three measurements for each test and average from the results using the following formula.
6. Perform the test for the following shifts in the same manner as in Step 5.
Evaluation of time lag test
|
Condition |
Possible cause |
|
|---|---|---|
|
N→D shift
|
More than specification
|
• Low line pressure
• Forward clutch slipping
• Oil leaking from forward clutch fluid circuit
• Shift solenoid A not operating properly
|
|
Less than specification
|
• Forward accumulator not operating properly
• Shift solenoid A not operating properly
• Excessive line pressure
|
|
|
N→R shift
|
More than specification
|
• Low line pressure
• Low and reverse brake slipping
• Reverse clutch slipping
• Shift solenoid B not operating properly
|
|
Less than specification
|
• Servo apply accumulator not operating properly
• Shift solenoid B not operating properly
• Excessive line pressure
|
|