Disassembly

DISASSEMBLY
1. REMOVE CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR ASSEMBLY
Remove the bolt and sensor assembly.
2. REMOVE VALVE LIFTERS AND SHIMS
HINT: Arrange the valve lifters and shims in the correct order.
3. REMOVE VALVES

a. Using SST, compress the valve spring and remove the 2 keepers.
SST 09202-70020 (09202-00010)
b. Remove the spring retainer, valve spring, valve and spring seat.
HINT: Arrange the valves, valve springs, spring seats and spring retainers in the correct order.

c. Using needle-nose pliers, remove the oil seal.
INSPECTION
1. CLEAN TOP SURFACES OF PISTONS AND CYLINDER BLOCK

a. Turn the crankshaft, and bring each piston to Top Dead Center (TDC). Using a gasket scraper, remove all the carbon from the piston top surface.

b. Using a gasket scraper, remove all the gasket material from the cylinder block surface.
c. Using compressed air, blow carbon and oil from the bolt holes.
CAUTION: Protect your eyes when using high-pressure compressed air.
2. INSPECT TOP SURFACE OF CYLINDER BLOCK FOR FLATNESS
3. CLEAN CYLINDER HEAD

a. Using a gasket scraper, remove all the gasket material from the cylinder block contact surface.
NOTICE: Be careful not to scratch the cylinder block contact surface.

b. Using a wire brush, remove all the carbon from the combustion chamber.
NOTICE: Be careful not to scratch the cylinder block contact surface.
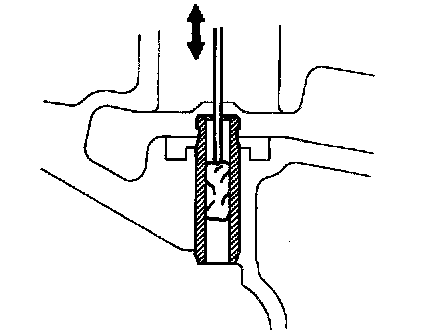
c. Using a valve guide bushing brush and solvent, clean all the guide bushings.
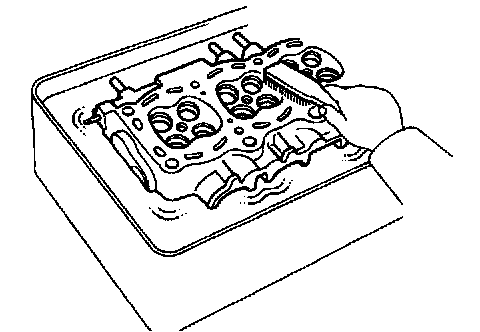
d. Using a soft brush and solvent, thoroughly clean the cylinder head.
4. INSPECT CYLINDER HEAD

a. Inspect for flatness.
Using a precision straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the surfaces contacting the cylinder block and the manifolds for warpage.

Maximum warpage:
If warpage is greater than maximum, replace the cylinder head.

b. Inspect for cracks. Using a dye penetrant, check the combustion chamber, intake ports, exhaust ports and cylinder block surface for cracks. If cracked, replace the cylinder head.

5. CLEAN VALVES
a. Using a gasket scraper, chip off any carbon from the valve head.
b. Using a wire brush, thoroughly clean the valve.
6. INSPECT VALVE STEMS AND GUIDE BUSHINGS

a. Using a caliper gauge, measure the inside diameter of the guide bushing.
Bushing inside diameter: 6.010 - 6.030 mm (0.2366 - 0.2374 inch)

b. Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of the valve stem.

Valve stem diameter:
c. Subtract the valve stem diameter measurement from the guide bushing inside diameter measurement.

Standard oil clearance:

Maximum oil clearance:
If the clearance is greater than maximum, replace the valve and guide bushing.
7. INSPECT AND GRIND VALVES

a. Grind the valve enough to remove pits and carbon.
b. Check that the valve is ground to the correct valve face angle.
Valve face angle: 44.5°

c. Check the valve head margin thickness.
Standard margin thickness: 0.8 - 1.2 mm (0.031 - 0.047 inch)
Minimum margin thickness: 0.5 mm (0.020 inch)
If the margin thickness is less than minimum, replace the valve.
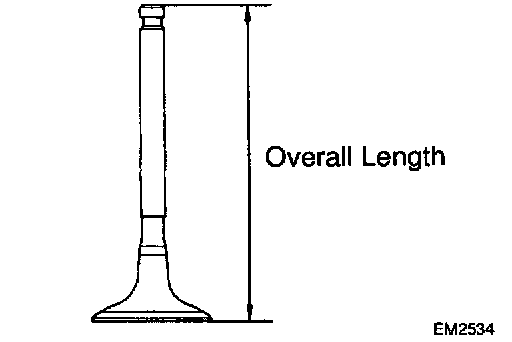
d. Check the valve overall length.

Standard overall length:

Minimum overall length:
If the overall length is less than minimum, replace the valve.

e. Check the surface of the valve stem tip for wear.
If the valve stem tip is worn, resurface the tip with a grinder or replace the valve.
NOTICE: Do not grind off more than the minimum length.
8. INSPECT AND CLEAN VALVE SEATS

a. Using a 45° carbide cutter, resurface the valve seats.
Remove only enough metal to clean the seats.

b. Check the valve seating position. Apply a light coat of Prussian blue (or white lead) to the valve face. Lightly press the valve against the seat. Do not rotate valve.
c. Check the valve face and seat for the following:
^ If blue appears 360° around the face, the valve is concentric. If not, replace the valve.
^ If blue appears 360 around the valve seat, the guide and face are concentric. If not, resurface the seat.
^ Check that the seat contact is in the middle of the valve face with the following width: 1.0 - 1.4 mm (0.039 - 0.055 inch)
If not, correct the valve seats as follows:

1. If the seating is too high on the valve face, use 30° and 45° cutters to correct the seat.

2. If the seating is too low on the valve face, use 75° and 45° cutters to correct the seat.

d. Hand-lap the valve and valve seat with an abrasive compound.
e. After hand-lapping, clean the valve and valve seat.
9. INSPECT VALVE SPRINGS

a. Using a steel square, measure the deviation of the valve spring.
Maximum deviation: 2.0 mm (0.079 inch)
If the deviation is greater than maximum, replace the valve spring.

b. Using a vernier caliper, measure the free length of the valve spring.
Free length: 40.95 - 42.80 mm (1.6122 - 1.6850 inch)
If the free length is not as specified, replace the valve spring.

c. Using a spring tester, measure the tension of the valve spring at the specified installed length.
Installed tension: 164 - 189 N (16.7- 19.3 kgf, 36.8 - 42.5 lbs.) at 34.7 mm (1.366 inch)
If the installed tension is not as specified, replace the valve spring.
10. INSPECT CAMSHAFTS

a. Inspect the circle runout.
1. Place the camshaft on V-blocks.
2. Using a dial indicator, measure the circle runout at the center journal.
Maximum circle runout: 0.04 mm (0.0016 inch)
If the circle runout is greater than maximum, replace the camshaft.

b. Using a micrometer, measure the cam lobe height.

Standard cam lobe height:

Minimum cam lobe height:
If the cam lobe height is less than minimum, replace the camshaft.

c. Using a micrometer, measure the journal diameter.
Journal diameter: 26.959 - 26.975 mm (1.0614 - 1.0620 inch)
If the journal diameter is not as specified, check the oil clearance.

d. Using vernier calipers, measure the free distance between the gear spring ends.
Free distance: 22.5 - 22.9 mm (0.886 - 0.902 inch)
If the free distance is not as specified, replace the gear spring.

e. Inspect the journal oil clearance.
1. Clean the bearing caps and camshaft journals.
2. Check that bearings for flaking and scoring. If the bearings are damaged, replace the bearing caps and cylinder head as a set.
3. Place the camshafts on the cylinder head.
4. Lay a strip of Plastigage across each of the camshaft journals.
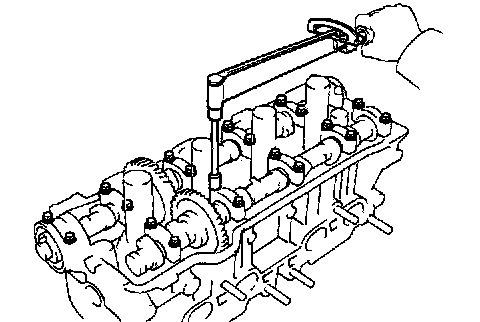
5. Install the bearing caps.
NOTICE: Do not turn the camshaft.
6. Remove the bearing caps.

7. Measure the Plastigage at its widest point.
Standard oil clearance: 0.025 - 0.062 mm (0.0010 - 0.0024 inch)
Maximum oil clearance: 0.10 mm (0.0039 inch)
If the oil clearance is greater than maximum, replace the camshaft. If necessary, replace the bearing caps and cylinder head as a set.
8. Completely remove the Plastigage.

f. Inspect the camshaft thrust clearance.
1. Install the camshaft.
2. Using a dial indicator, measure the thrust clearance while moving the camshaft back and forth.

Standard thrust clearance:

Maximum thrust clearance:
If the thrust clearance is greater than maximum, replace the camshaft. If necessary, replace the bearing caps and cylinder head as a set.

g. Inspect the camshaft gear backlash.
1. Install the camshafts without installing the exhaust cam sub-gear.
2. Using a dial indicator, measure the backlash.
Standard backlash: 0.020 - 0.200 mm (0.0008 - 0.0079 inch)
Maximum backlash: 0.30 mm (0.0188 inch)
If the backlash is greater then maximum, replace the camshafts.
11. INSPECT VALVE LIFTERS AND LIFTER BORES

a. Using a caliper gauge, measure the lifter bore diameter of the cylinder head.
Lifter bore diameter: 31.000 - 31.018 mm (1.2205 - 1.2212 inch)

b. Using a micrometer, measure the lifter diameter.
Lifter diameter: 30.96 - 30.976 mm (1.2191 - 1.2195 inch)
Subtract the lifter diameter measurement from the lifter bore diameter measurement.
Standard oil clearance: 0.024 - 0.052 mm (0.0009 - 0.0020 inch)
Maximum oil clearance: 0.07 mm (0.0028 inch)
If the oil clearance is greater than maximum, replace the lifter. If necessary, replace the cylinder head.

12. INSPECT INTAKE MANIFOLD
Using a precision straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the surface contacting the cylinder head for warpage.
Maximum warpage: 0.30 mm (0.0118 inch)
If warpage is greater than maximum, replace the manifold.

13. INSPECT EXHAUST MANIFOLD
Using a precision straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the surface contacting the cylinder head for warpage.
Maximum warpage: 0.30 mm (0.0118 inch)
If warpage is greater than maximum, replace the manifold.
REPLACEMENT
REPLACE VALVE GUIDE BUSHINGS

a. Gradually heat the cylinder head to 80 - 100°C (176 - 212°F).

b. Using SST and a hammer, tap out the guide bushing.
SST 09201-10000 (09201-01060), 09950-70010 (09951-07100)

c. Using a caliper gauge, measure the bushing bore diameter of the cylinder head.

d. Select a new guide bushing (STD or O/S 0.05). If the bushing bore diameter of the cylinder head is greater than 11.012 mm (0.4335 inch), machine the bushing bore to the following dimension: 11.035 - 11.062 mm (0.4344 - 0.4355 inch) If the bushing bore diameter of the cylinder head is greater than 11.062 mm (0.4355 inch), replace the cylinder head.

HINT: Different the bushings are used for the intake and exhaust.
e. Gradually heat the cylinder head to 80 - 100°C (176 - 212°F).

f. Using SST and a hammer, tap in a new guide bushing until there is 8.0 - 8.8 mm (0.315 - 0.346 inch) protruding from the cylinder head.
SST 09201-10000 (09201-01060), 09950-70010 (09951-07100)

g. Using a sharp 6 mm reamer, ream the guide bushing to obtain the standard specified clearance between the guide bushing and valve stem.