VARIABLE VALVE TIMING MECHANISM [SKYACTIV-G 1.3, SKYACTIV-G 1.5 (WITH 4-1 EXHAUST SYSTEM)]
id0110q30020q4
Outline
• The variable valve timing mechanism changes the valve timing.
• By optimizing the change in the valve timing, the internal EGR amount and effective compression ratio are controlled, pumping loss is reduced, and the combustion is controlled optimally.
• A hydraulic pressure type variable valve timing mechanism has been adopted on the intake side.
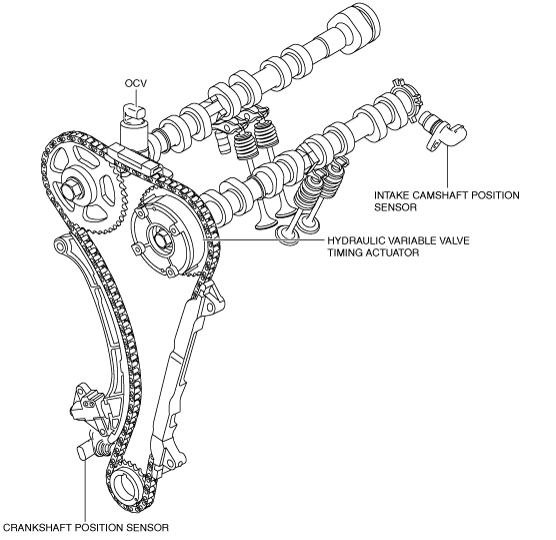
Structural View
Structure
|
Part name
|
Function
|
|
Hydraulic variable valve timing actuator
|
|
|
OCV
|
|
|
Intake camshaft position sensor
|
|
|
Crankshaft position sensor
|
|
Operation
• The variable valve timing mechanism has the following four modes:
• The four modes are determined by the operation of the OCV and hydraulic variable valve timing actuator.
|
Mode
|
OCV operation
(spool valve)
|
Hydraulic pressure
|
Hydraulic variable valve timing
actuator operation
|
Valve timing
|
|
Stopper pin
|
Rotor
|
|
Fixed mode
|
Maximum retard position
|
To retard chamber
|
×
|
Maximum retard position
|
Maximum retard
|
|
Advance mode
|
To advance side
|
To advance chamber
|
—
|
Move to advance side
|
Advance
|
|
Retard mode
|
To retard side
|
To retard chamber
|
—
|
Move to retard side
|
Retard
|
|
Hold mode
|
Middle point
|
To advance/retard chamber
|
—
|
Hold at optimum position
|
Hold at optimum position
|
× :Engages with rotor depression
— :Disengages from rotor depression
Fixed mode
-
• The rotor depression at the maximum retard position and the stopper pin in the hydraulic variable valve timing actuator are engaged by the spring force. Due to this, the housing (intake camshaft sprocket) and the rotor (intake camshaft) rotate as a single unit.
Advance mode
-
• The spool valve in the OCV moves to the advance side and hydraulic pressure is applied to the advance chamber in the hydraulic variable valve timing actuator by a signal from the PCM. Due to this, the rotor (intake camshaft) rotates in the advance direction relative to the housing (intake camshaft sprocket), and the valve timing is advanced.
Retard mode
-
• The spool valve in the OCV moves to the retard side and hydraulic pressure from the oil pump is applied to the retard chamber by a signal from the PCM. Due to this, the rotor (intake camshaft) rotates in the retard direction relative to the housing (intake camshaft sprocket), and the valve timing is retarded.
Hold mode
-
• The spool valve in the OCV is positioned the area around the middle point at advance and retard by a signal from the PCM. At this time, hydraulic pressure is applied to both of the advance and retard chambers in the variable valve timing actuator. Due to this, there is no change in the relative angle of the rotor (intake camshaft) and the housing (intake camshaft sprocket) and the current valve timing is held.
-
Note
-
• To switch to the fixed mode (lock-pin in hydraulic variable valve timing actuator engaged with rotor depression) when the ignition is switched OFF (LOCK), the engine stop condition is extended (within approx. 0.5 s) under the following conditions: Due to this, engine re-startability has been improved. (ATX)
-
― During or right after fast idle increase (during control of catalytic converter earlier activation)
― Right after operating to D/R/M position while the vehicle is parked at high-altitude, or operating from D/R/M position to P/N position