MECHANICAL [SKYACTIV-X 2.0]
id0110hf000100
Outline
• The sliding resistance*1 has been reduced by:
-
― Adoption of a rocker arm (built in needle roller bearing)
― Reducing the valve spring load
― Narrowing down the crankshaft journal
― Optimizing the piston skirt shape
― Adoption of a low-tension piston ring
― Lowered tensioning of the drive belt
• A maintenance-free design for valve clearance has been achieved with the adoption of the HLA.
• With the adoption of a piston cavity, cooling loss has been reduced.
• The pumping loss*2 has been reduced with the adoption of the variable valve timing mechanism on both sides of the intake and exhaust.
• The timing chain behavior has been stabilized and sliding resistance has been reduced by optimizing the shape and rigidity of the timing chain-related parts.
• Fuel economy in the low/middle load range has been improved by achieving compression ignition.
• Pumping loss*2 reduction and cooling loss reduction in the combustion process due to a decrease in the combustion temperature have been achieved by burning a lean air-fuel mixture.
*1 :Resistance (friction force) which occurs when two object slide against each other. The larger the sliding resistance, the greater the energy loss.
*2 :Energy loss which occurs from each type of resistance corresponding to intake and exhaust is called pumping loss.
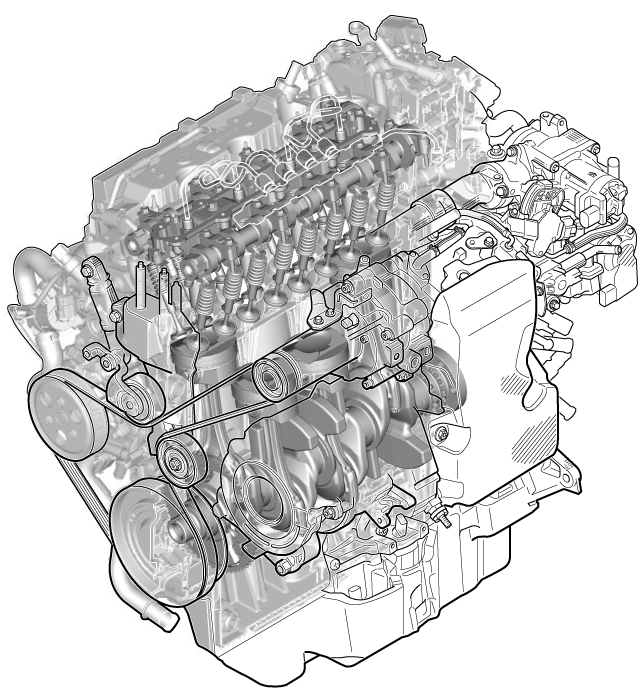
Structural View
Structure
• Consists of the following parts:
|
Part name
|
Reference
|
|
Cylinder head cover
|
―
|
|
Cylinder head
|
|
|
Cylinder head gasket
|
―
|
|
Cylinder block
|
―
|
|
Crankshaft
|
|
|
Piston
|
|
|
Connecting rod
|
|
|
Engine rear cover
|
|
|
Crankshaft pulley
|
|
|
Drive belt
|
|
|
Valve mechanism
|
Valve
|
|
|
HLA
|
|
|
Camshaft
|
|
|
Timing chain
|
|
|
Variable valve timing mechanism
|
Intake electric variable valve timing actuator
|
―
|
|
Exhaust electric variable valve timing actuator
|
―
|
|
Intake electric variable valve timing relay
|
―
|
|
Exhaust electric variable valve timing relay
|
―
|
|
Engine mount
|
―
|