Powertrain Relay Diagnosis
Powertrain Relay Diagnosis
Circuit Description
The powertrain relay is a normally open relay. The relay armature is held in the open position by spring tension. Battery positive voltage is supplied directly to the relay coil and the armature contact at all times. The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies the ground path to the relay coil control circuit, via an internal integrated circuit called an output driver module (ODM). When the PCM commands the relay ON, the relay coil creates an electromagnetic field. This electromagnetic field overcomes the spring tension and pulls the armature contact into the stationary contact of the relay load circuit. The closing of the relay contacts allows current to flow from the battery to the following fuses and relay:
* IGN fuse
* Injectors fuse
* ECM/ETC fuse
* EMISS fuse
* After cooler pump relay
When the ignition switch is turned to the OFF position, power is interrupted to the ODM in the PCM, and the relay electromagnetic field collapses. This allows the spring tension to separate the relay armature contact from the relay load circuit contact, which interrupts current flow to the fuses.
If the powertrain relay fails to close, the engine will crank but will not run. The class 2 communications will be available with the use of a scan tool.
The powertrain relay system diagnosis table assumes that the vehicle battery is fully charged. Refer to Battery Inspection/Test. Battery Inspection/Test
Test
Step 1 - Step 7:
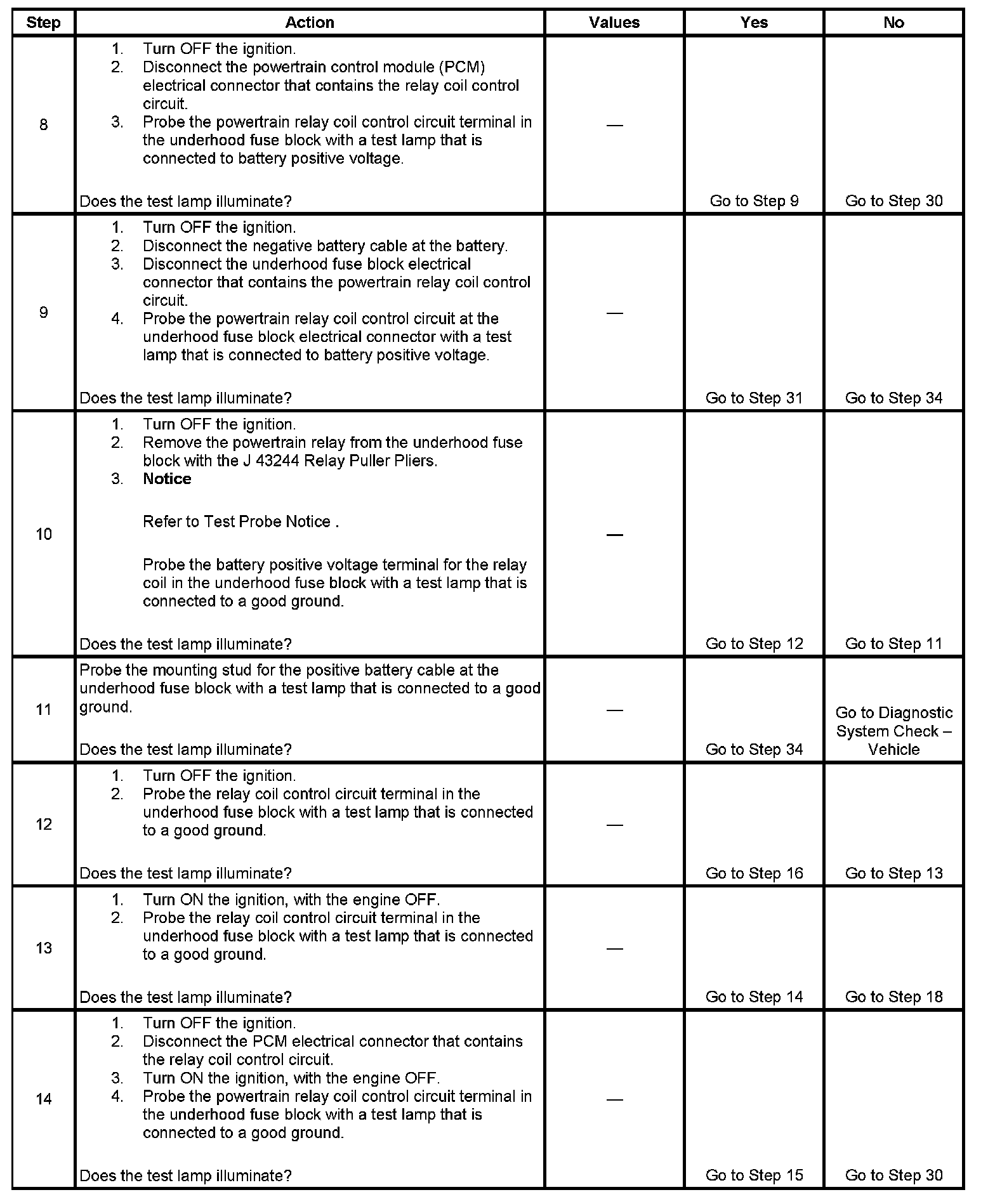
Step 8 - Step 14:
Step 15 - Step 19:

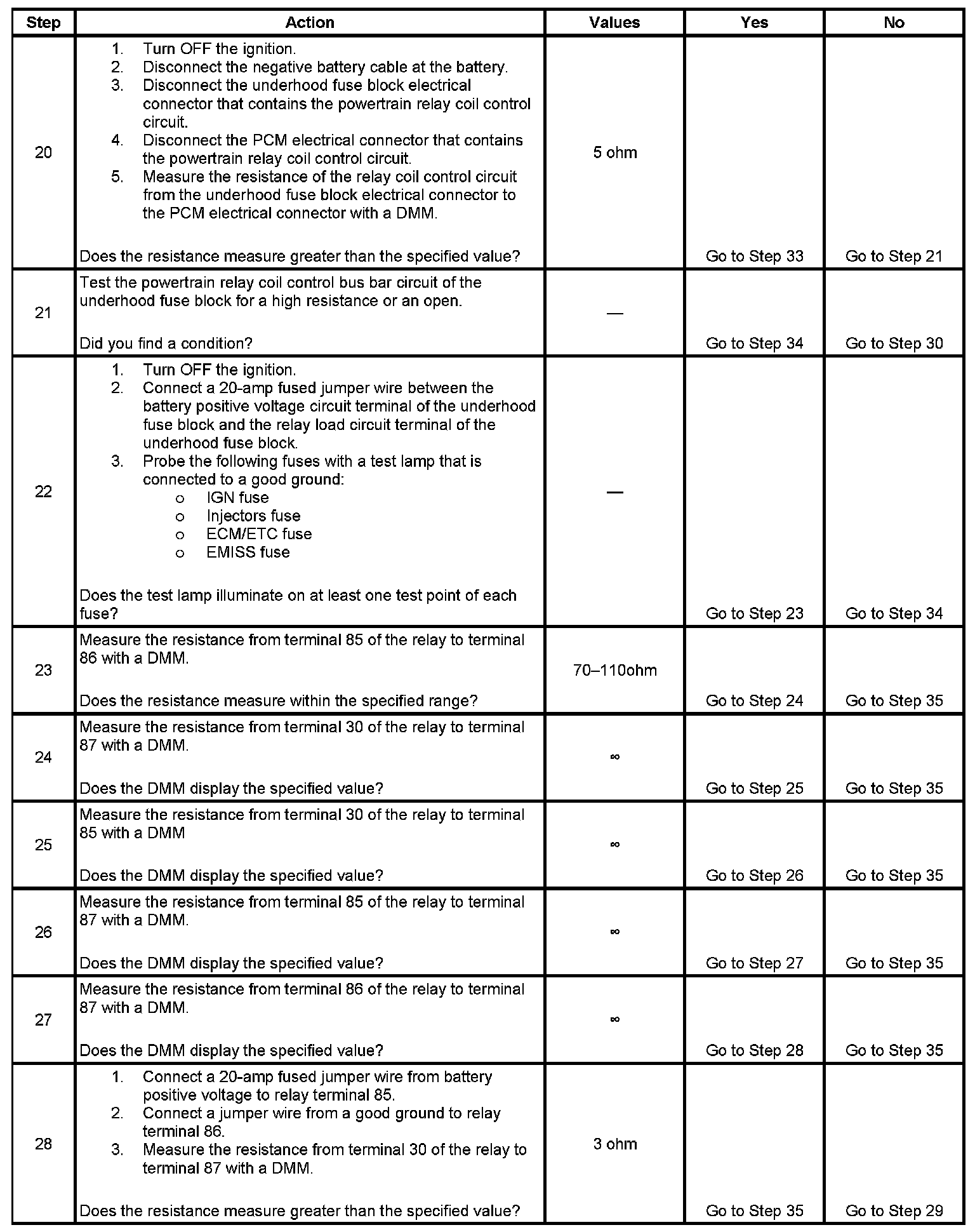
Step 20 - Step 28: