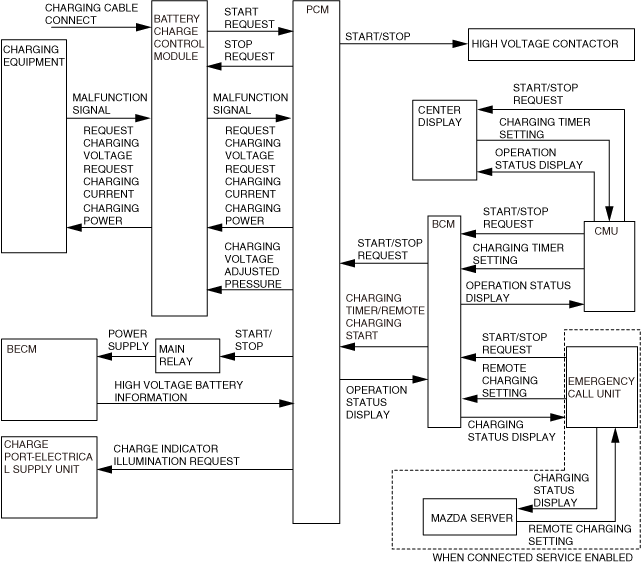
• When the high voltage contactors are turned on, the PCM sends charging power (during normal charging) signal or a transmission request signal (during fast charging) to the charging system. When the charging system receives this signal, it starts transmitting power for charging.
• If the charging time is set using the charging timer, the PCM puts the request to the charging system on hold. The body control module (BCM) sends a charging start request to the PCM when the start condition set on the charging timer is met. The PCM sends the request signal to the charging control unit after receiving the charging start request from the body control module (BCM).
• The PCM sends the requested charging current to the charging control unit based on the amount of current that can be output by the charging system, the high voltage battery temperature, and the power usage by auxiliary devices during charging.
• During normal charging, the onboard charger converts the AC voltage to DC voltage and regulates the voltage to be the same as the high voltage battery voltage.
• During charging, the PCM keeps the high voltage battery and the onboard charger at the right temperature by performing the following controls.
-