|
1
|
VERIFY DTC
• Perform the DTC inspection for the following modules.
-
― PCM
― TCM (ATX)
― DSC HU/CM
― Dash-electrical supply unit
― SAS control module
― Body control module (BCM)
• Are any DTCs displayed?
|
Yes
|
Repair the malfunctioning location according to the applicable DTC troubleshooting.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
2
|
DETERMINE INSPECTION LOCATION ACCORDING TO MALFUNCTION SYMPTOM
If i-stop function operates even though the i-stop warning light (amber) is turned on:
• Go to the next step.
If i-stop function operates even though the i-stop OFF switch is turned on:
• Go to Step 4.
If i-stop function operates (i-stop function operates while parking vehicle in a garage) even though the steering wheel is being operated:
• Go to Step 6.
If i-stop function operates even though the brake pedal is not depressed:
• Go to Step 7.
If i-stop function operates even though the hood is open:
• Go to Step 11.
If i-stop function operates even though the doors, trunk lid (4SD), or liftgate (5HB) is opened:
• Go to Step 13.
If i-stop function operates even though the seat belt is not fastened:
• Go to Step 16.
If i-stop function operates even though there is a steep slope:
• Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• If the CAN communication is normal, repeat the inspection from Step 1.
-
― If the malfunction recurs, replace the SAS control module, then perform the repair completion verification 1.
If i-stop function operates even though the ambient temperature is outside of the operation range:
• Go to Step 18.
If i-stop function operates even though the cabin temperature is outside of the operation range:
• Go to Step 21.
If i-stop function operates even though the A/C output is high:
• Go to Step 24.
If i-stop function operates even though the engine coolant temperature is outside of the operation range:
• Go to Step 25.
|
|
3
|
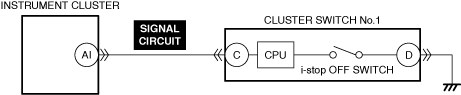
DETERMINE IF MALFUNCTION CAUSE IS CAN COMMUNICATION LINE BETWEEN INSTRUMENT CLUSTER AND PCM OR OTHER
• Access the instrument cluster PID I-STOP_OFF_SW during an engine stop by the i-stop control using the M-MDS.
• Is the PID value “off”?
|
Yes
|
i-stop warning light (amber) illumination circuit malfunction in instrument cluster can be considered.
• Replace the instrument cluster and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Malfunction in CAN communication circuit between instrument cluster and PCM can be considered.
• Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
4
|
INSPECT i-stop OFF SWITCH FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
5
|
INSPECT i-stop OFF SWITCH SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR SHORT CIRCUIT AND OPEN CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuit for a short circuit and open circuit.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• If the CAN communication is normal, repeat the inspection from Step 1.
-
― If the malfunction recurs, replace the instrument cluster, then perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
6
|
INSPECT EPS CONTROL MODULE FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Perform the following procedure:
1. Switch the ignition off, and after 2 min or more have elapsed, switch the ignition ON.
2. Start the engine and drive the vehicle 10 m {32 ft 10 in} or more in a straight line at a speed of 10 km/h {6.2 mph} or more.
3. Stop the vehicle with the wheels in the straight-ahead position.
4. Access the EPS control module PID STR_ANG using the M-MDS.
-
• If the STR_ANG value is normal, perform the repair completion verification 1. (Because the steering angle (estimated absolute angle) has returned to normal)
• If the STR_ANG value is not normal, replace the EPS control module, then perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
7
|
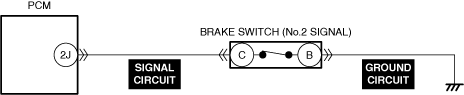
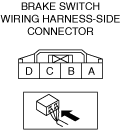
INSPECT BRAKE SWITCH FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
8
|
INSPECT BRAKE SWITCH SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO POWER SUPPLY
• Inspect the applicable circuit for a short to power supply.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
9
|
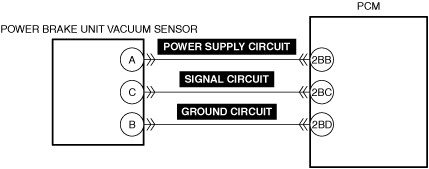
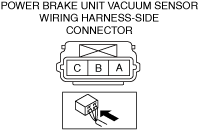
INSPECT POWER BRAKE UNIT VACUUM SENSOR FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
10
|
INSPECT POWER BRAKE UNIT VACUUM SENSOR POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT, SIGNAL CIRCUIT, AND GROUND CIRCUIT FOR SHORT CIRCUIT AND OPEN CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuit for a short circuit and open circuit.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• If the CAN communication is normal, repeat the inspection from Step 1.
-
― If the malfunction recurs, replace the PCM, then perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
11
|
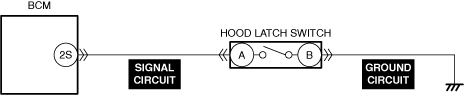
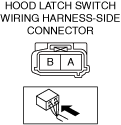
INSPECT HOOD LATCH SWITCH FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
12
|
INSPECT HOOD LATCH SWITCH SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND
• Inspect the applicable circuit for a short to ground.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• If the CAN communication is normal, repeat the inspection from Step 1.
-
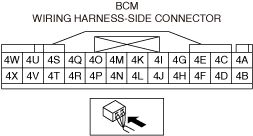
― If the malfunction recurs, replace the body control module (BCM), then perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
13*
|
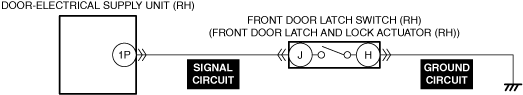
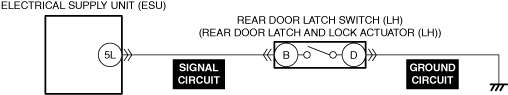
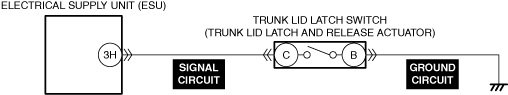
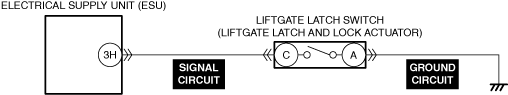
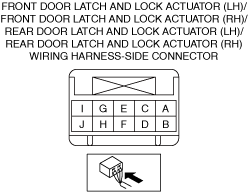
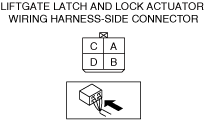
INSPECT DOOR LATCH SWITCH AND TRUNK LID LATCH SWITCH (4SD)/LIFTGATE LATCH SWITCH (5HB) FOR MALFUNCTION
• Switch the ignition ON (engine off).
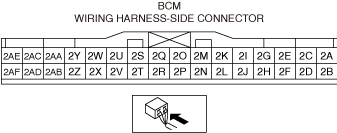
• Access the following body control module (BCM) PIDs using the M-MDS:
-
― DOOR_SW_ALL (all door latch switches)
― DOOR_SW_D (driver-side door latch switch)
― DOOR_SW_L/R (rear door latch switch (LH))
― DOOR_SW_P (passenger-side door latch switch)
― DOOR_SW_R/R (rear door latch switch (RH))
― T/LGT_SW (trunk lid latch switch (4SD)/liftgate latch switch (5HB))
• Inspect the switch which the open/close operation of the doors, trunk lid (4SD), or liftgate (5HB) is not in conjunction with the PID value.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
If DOOR_SW_ALL, DOOR_SW_D, DOOR_SW_L/R, or DOOR_SW_R/R PID has a malfunction:
• Go to the next step.
If T/LGT_SW PID has a malfunction:
• Go to Step 15.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
14
|
INSPECT DOOR LATCH SWITCH SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND
• Inspect the PID-related switch circuit in which the malfunction occurred in Step 13 for a short to ground.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• If the CAN communication is normal, repeat the inspection from Step 1.
-
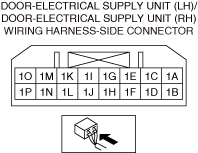
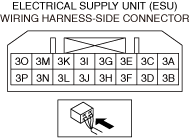
― If the malfunction recurs, replace the door-electrical supply unit, electrical supply unit (ESU), or body control module (BCM) then perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
15
|
INSPECT TRUNK LID LATCH SWITCH (4SD)/LIFTGATE LATCH SWITCH (5HB) SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuit for an open circuit.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• If the CAN communication is normal, repeat the inspection from Step 1.
-
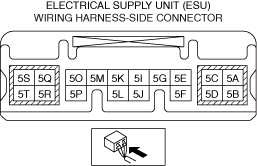
― If the malfunction recurs, replace the electrical supply unit (ESU), then perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
16
|
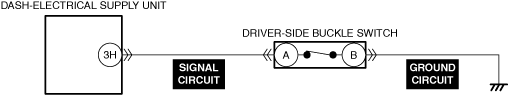
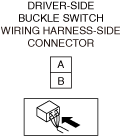
INSPECT DRIVER-SIDE BUCKLE SWITCH FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
17
|
INSPECT DRIVER-SIDE BUCKLE SWITCH SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuit for an open circuit.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• If the CAN communication is normal, repeat the inspection from Step 1.
-
― If the malfunction recurs, replace the dash-electrical supply unit, then perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
18
|
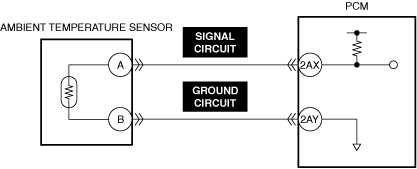
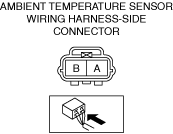
INSPECT AMBIENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
19
|
INSPECT AMBIENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR SHORT CIRCUIT AND OPEN CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuit for a short circuit and open circuit.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
20
|
INSPECT AMBIENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR GROUND CIRCUIT FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuit for an open circuit.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• If the CAN communication is normal, repeat the inspection from Step 1.
-
― If the malfunction recurs, replace the PCM, then perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
21
|
INSPECT PASSENGER COMPARTMENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
22
|
INSPECT PASSENGER COMPARTMENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR SHORT CIRCUIT AND OPEN CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuit for a short circuit and open circuit.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
23
|
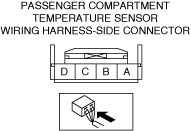
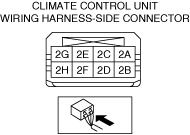
INSPECT PASSENGER COMPARTMENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR GROUND CIRCUIT FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuit for an open circuit.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• If the CAN communication is normal, repeat the inspection from Step 1.
-
― If the malfunction recurs, replace the climate control unit, then perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
24
|
INSPECT DRIVER-SIDE AIR MIX ACTUATOR FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Inspect the air mix door and linkage for sticking.
If there is no malfunction:
• Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
-
― If the CAN communication is normal, repeat the inspection from Step 1.
-
• If the malfunction recurs, replace the dash-electrical supply unit, then perform the repair completion verification 1.
If there is any malfunction:
• Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
25
|
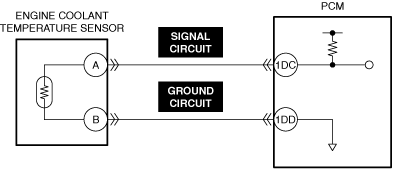
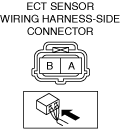
INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part.
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
26
|
INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL CIRCUIT AND GROUND CIRCUIT FOR SHORT CIRCUIT AND OPEN CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuit for a short circuit and open circuit.
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• If the CAN communication is normal, repeat the inspection from Step 1.
-
― If the malfunction recurs, replace the PCM, then perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification 1.
|
|
Repair completion verification 1
|
VERIFY THAT VEHICLE IS REPAIRED
• Install/connect the part removed/disconnected during the troubleshooting procedure.
• Has the malfunction symptom been eliminated?
|
Yes
|
Complete the symptom troubleshooting. (Explain contents of repair to customer)
|
|
No
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
• If the CAN communication is normal, perform the diagnosis from Step 1.
-
― If the malfunction recurs, go to the next step.
|
|
Repair completion verification 2
|
VERIFY IF MALFUNCTION IS CAUSED BY NOT PERFORMING PCM REPROGRAMMING
• Verify repair information and verify that there is a new calibration in the PCM.
• Is there a new calibration in the PCM?
|
Yes
|
Perform the PCM reprogramming and verify if the malfunction symptom was corrected.
• If the malfunction recurs, replace the PCM.
|
|
No
|
Replace the PCM.
|