AIR CHARGING SYSTEM [SKYACTIV-D 2.2]
id0113z7706400
Purpose, Outline
Fuel injector (2pin type)
-
• The two-stage turbocharger selectively operates according to driving conditions to realize low emissions, low fuel consumption, high torque, and high response.
• To obtain efficient, high air charging in a wide range of driving conditions, the large-type turbocharger and the small-type turbocharger perform two-stage air charging in the low engine speed range, and only the large-type turbocharger performs air charging in the high engine speed range.
Fuel injector (6pin type)
-
• To realize low emission, low fuel consumption, high torque, and high response, either one of the two turbochargers is used depending on the driving range.
• To attain efficient, high boost pressure in various driving ranges, two-stage boost is performed in the low engine speed range using the large-type turbocharger and the small-type turbocharger, and boost is performed in the high engine speed range only using the large-type turbocharger.
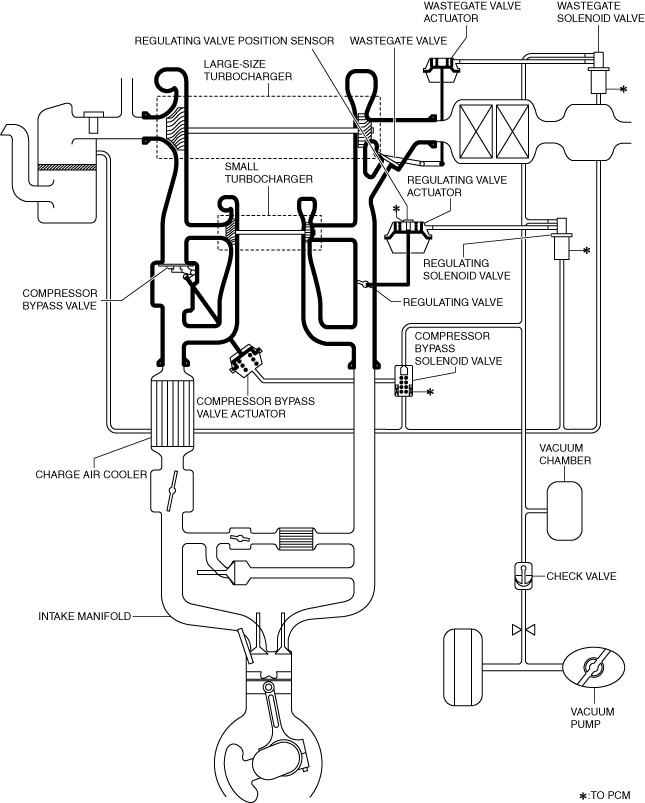
System diagram
Fuel injector (2pin type)
Fuel injector (6pin type)
Structure
• The air charging system consists of the following parts.
|
Part name
|
Reference
|
|
Turbocharger
|
Large-type turbocharger
|
|
|
Small-type turbocharger
|
|
Compressor bypass valve
|
|
Compressor bypass valve actuator
|
|
Regulating valve
|
|
Regulating valve actuator
|
|
Wastegate valve (fuel injector (2pin type))
|
|
Wastegate valve actuator (fuel injector (2pin type))
|
|
Variable turbine geometry turbocharger actuator (6pin type))
|
|
Compressor bypass solenoid valve
|
|
|
Regulating solenoid valve (fuel injector (2pin type))
|
|
|
Wastegate solenoid valve (fuel injector (2pin type))
|
|
|
Vacuum chamber (fuel injector (2pin type))
|
|
|
Check valve
|
|
|
Charge air cooler
|
|
Operation
Fuel injector (2pin type)
-
• The two-stage air charging system is divided between the large-type turbocharger and small-type turbocharger for control in mainly 5 ranges.
-
1. Engine starting/partial warmup region range
-
• For the purpose of earlier activation of the catalytic converter, air charging by the small-type turbocharger and large-type turbocharger is stopped. By stopping the air charging, the exhaust gas arrives at the catalytic converter as is with no loss of exhaust heat because it does not contact the turbine.
-
2. Low engine speed range
-
• At low engine speeds, the air charging effect by the large-type turbocharger is small because the force of the exhaust gas is small. By connecting the small-type turbocharger and large-type turbocharger in tandem and having the air charged by the large-type turbocharger further charged at the small-type turbocharger, air charging pressure is assured and high torque at the low engine speed range and high response are achieved.
-
3. Middle engine speed range
-
• In the range bordering between the low engine speed range and the high engine speed range, the regulating valve opens and closes according to the conditions. By opening and closing the valve, generation of turbocharger lag is suppressed by switching the operation of the small-type turbocharger.
-
4. High engine speed range
-
• In the high engine speed range, the small-type turbocharger is avoided because a larger amount of air is required, and only the large-type turbocharger performs air charging. By circumventing the small-type turbocharger, intake air resistance is small, and the charged air is efficiently taken in.
-
5. Air charging pressure excess region
-
• In the region where air charging pressure increases, the rise in air charging pressure is suppressed by opening and closing the wastegate valve to switch the air charging of the large-type turbocharger.
Fuel injector (6pin type)
-
• The two-stage boost system is divided between the large-type turbocharger and small-type turbocharger for control in mainly 3 regions.
-
1. Low engine speed range
-
• Because the amount of the exhaust gas introduced to the turbine in the low engine speed range is low, boost pressure is assured by connecting the small-type turbocharger and the large-type turbocharger in tandem and having the air charged by the large-type compressor further charged at the small-type compressor, and low emission, low fuel consumption, high torque, and high response are achieved.
-
2. Middle engine speed range
-
• In the range bordering where the operation switches between the two turbochargers, the regulating valve opening angle is controlled according to the conditions. High pressure boost is maintained by controlling the amount of exhaust gas introduced to the small-type turbocharger.
-
3. High engine speed range
-
• In the high engine speed range, only the large-type turbocharger performs air charging because a larger amount of air is required. By circumventing the small-type turbocharger, intake air resistance is small, and the charged air is efficiently taken in.